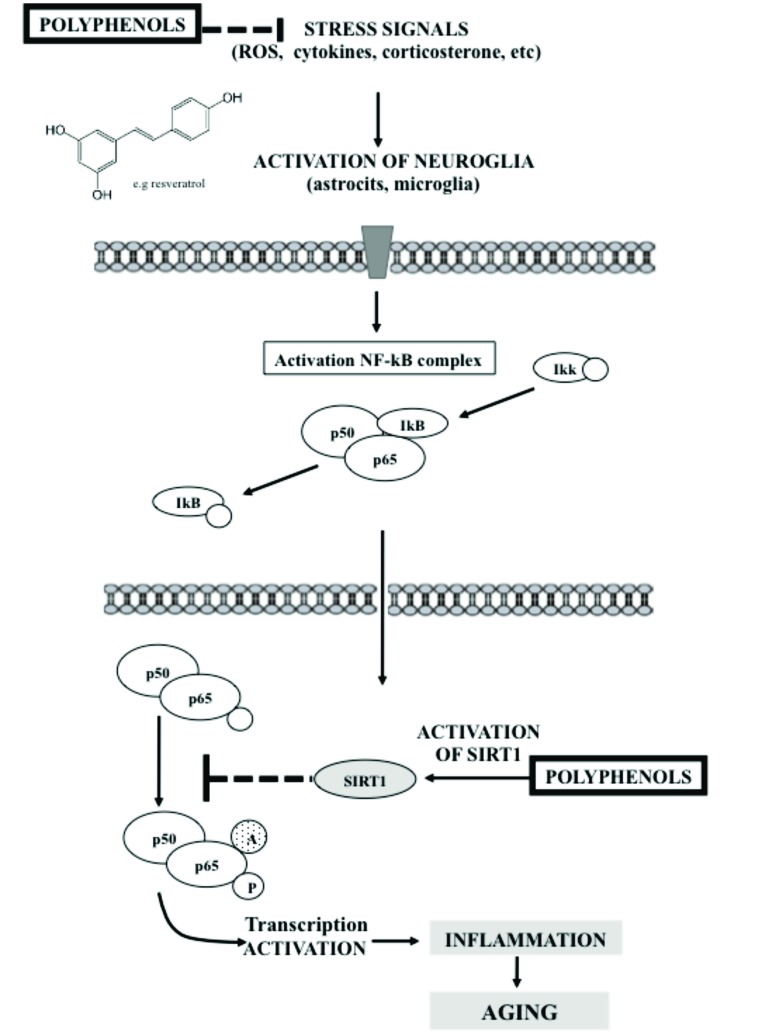
Fig. (1).
Scheme of the effect of polyphenols on SIRT1 and NF-κB signaling pathway involved in neuroinflammation. Stress signals as cytokines and ROS activate astrocytes and microglia, stimulating NF-κB signaling pathway, which leads to transcription of proinflammatory genes. This cascade of intracellular events results in increased cytokine production, ROS generation, inflammation, tissue damage and aging. Polyphenols (i.e resveratrol) can reduce the level of stress signals such as ROS, by avoiding oxidative stress, and citokines by activating and protecting SIRT1, which in turns cause a suppression of inflammation. SIRT1 directly inhibits NF-κB (by deacetylating the RelA/p65 subunit at lysine 310); preventing transcription activation of proinflammatory genes.