Fig. 1.
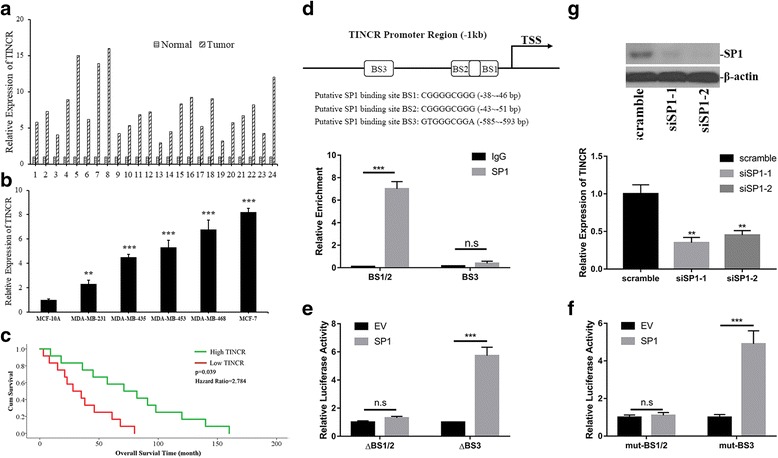
SP1 mediated overexpression of TINCR in human breast cancer. a The expression of TINCR was determined by real-time PCR and normalized to β-actin in human breast cancer samples (n = 24 pairs); b Relative expression of TINCR was measured by real-time PCR in human breast cancer cell line panel (n = 5) in comparison with immortalize human mammary epithelial cell line (MCF-10A). **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; c Kaplan-Meier curve of cumulative survival in breast cancer patients with high TINCR (n = 12) and low TINCR expression (n = 12). d The putative SP1 binding sites (BSs) across TINCR promoter predicted with PROMO (upper), the direct binding was demonstrated by SP1 enriched BS1/2 locus in ChIP assay (lower). e Dual-luciferase reporter assay with co-transfection of SP1 and TINCR promoter-driven luciferase plasmids carrying indicated deletion. ***p < 0.001, n.s: no significance. f Dual-luciferase reporter assay with co-transfection of SP1 and TINCR promoter-driven luciferase plasmids with scramble mutant in indicated regions. ***p < 0.001, n.s: no significance. g SP1 knockdown efficiency was evaluated by immunoblotting with β-actin as loading control. The relative expression of TINCR was determined by real-time PCR. **p < 0.01
