Table 2. The parent-structure formulae from the ICSD compounds identified by analogy that led to the lowest energy structures after DFT relaxation are shown along with the energies above the convex hull (Eanalogyhull), and the corresponding energies predicted after global structure search (Eglobalhull). The estimated bandgaps from SSEs (ESSEg) used at the beginning of the workflow, bandgaps (Eg), electron affinities (EA) and ionisation potentials (IP) calculated using a hybrid exchange-correlation functional at the end of the screening workflow, and effective masses for carrier electrons and holes from GGA calculations ( and
and  ) are also displayed.
) are also displayed.
| Compound | Parent | E analogy hull (meV per atom) | E global hull (meV per atom) | E SSE g (eV) | E g (eV) | EA (eV) | IP (eV) |
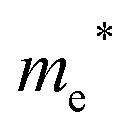
|

|
| Sn5S4Cl2 | Hg5 (O2Cl)2 | 96.5 | 61.8 | 2.0 | 0.91 | 3.30 | 4.21 | 0.50 | 0.40 |
| Sn4SF6 | Hg4OF6 | 51.8 | 46.7 | 2.0 | 3.36 | 2.45–2.94 a | 5.81–6.30 a | 0.86 | 2.01 |
| Cd5S4Cl2 | Hg5 (O2Cl)2 | 83.5 | 50.2 | 1.9 | 2.75 | 3.33 | 6.08 | 0.18 | 2.58 |
| Cd4SF6 | Cd4F6O | 18.2 | 18.0 | 1.9 | 2.15 | 4.33 | 6.48 | 0.25 | 2.00 |
aWhen only polar surfaces could be found, a dipole correction term was added to the calculation of the surface dipole, which yields upper and lower bounds to the EA and IP values (see Computational methods section).
