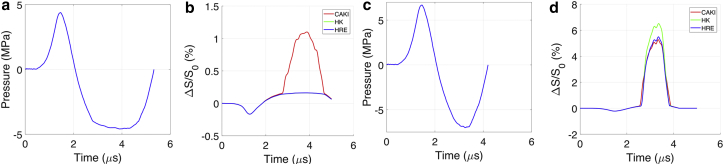
Figure 5.
(a) First proposed shock loading with a maximal tensile pressure of 4.59 MPa. (b) The resultant cell membrane strain is shown in three cell types. (c) The second proposed shock loading has a maximal tensile pressure of 7 MPa. (d) The resultant cell membrane strain is shown in three cell types. To see this figure in color, go online.