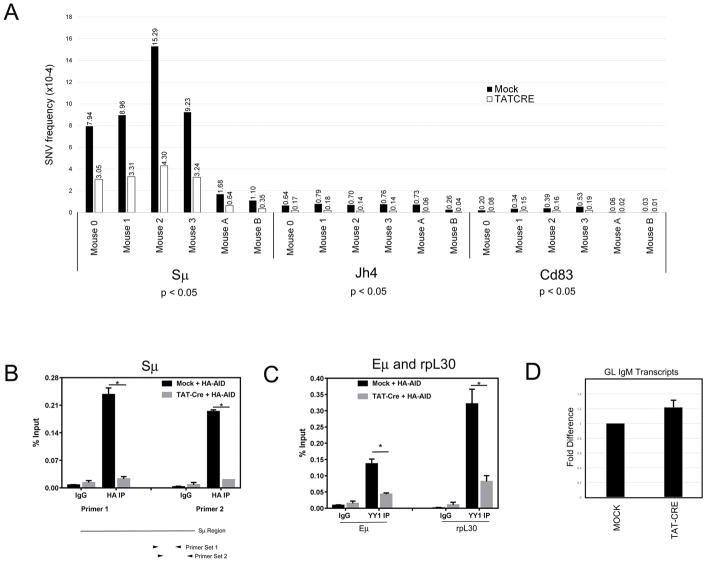
Figure 2.
YY1 effect on AID mediated mutations and AID genomic localization in ex vivo stimulated splenic B cells from yy1f/f mice. (A) Frequencies of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in Sμ, Jh4, and Cd83 promoter regions detected by NGS. Splenic B cells isolated from six individual yy1f/f mice were either mock treated or treated with TAT-CRE to delete the yy1 gene. After induction for 4 days with LPS plus IL4, DNA was isolated and DNA sequences at the Sμ, Jh4, and CD83 promoter were subjected to NGS DNA sequencing. The frequencies of single nucleotide varients are shown in mock treated (black columns) or TAT-CRE treated (white columns) mice. Differences between mock and TAT-CRE were calculated using the Wilcoxon test. (B and C) Recruitment of AID to the Sμ region, and YY1 to the Eμ enhancer and rpL30 promoter. Mock and TAT-CRE treated splenic yy1f/f B cells were transduced with retroviral vector pMX-HA-AID, and two days later cells were subjected to ChIP with control anti-IgG or anti-HA antibody (B), or YY1 antibody (C). QPCR was performed with primers that amplify the IgH Sμ region (B) or Eμ enhancer and rpL30 promoter (C). Error bars indicate standard deviation from the mean, and asterisks indicate p<0.001 in a two tailed T-test. (D) Quantitative RT-PCR of IgM germline transcripts in mock and TAT-CRE treated samples. RNA isolated from Mock and TAT-CRE treated samples was evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR with primers that detect the germline IgM transcript. Data are from six independent experiments and error bars show the standard deviation of the mean.