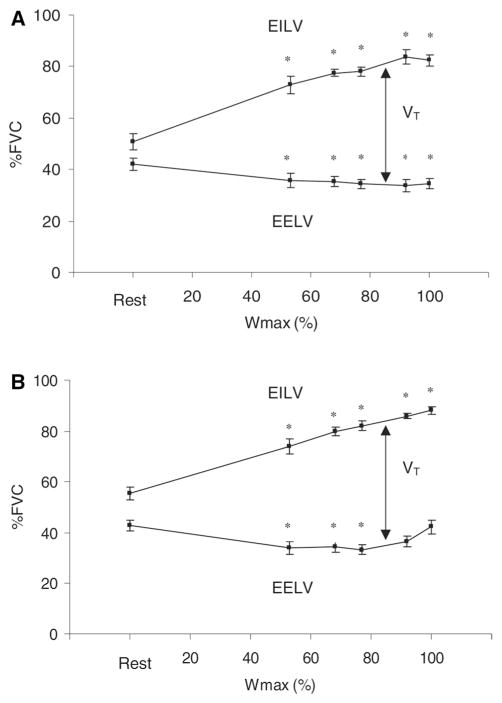
Fig. 1.
End-inspiratory lung volume (EILV), end-expiratory lung volume (EELV), and tidal volume (VT), expressed as a percentage of forced vital capacity (FVC) at rest and during progressive exercise to maximal workload at V̇O2max (Wmax) in men (a) and women (b) [38]. Reprinted with permission