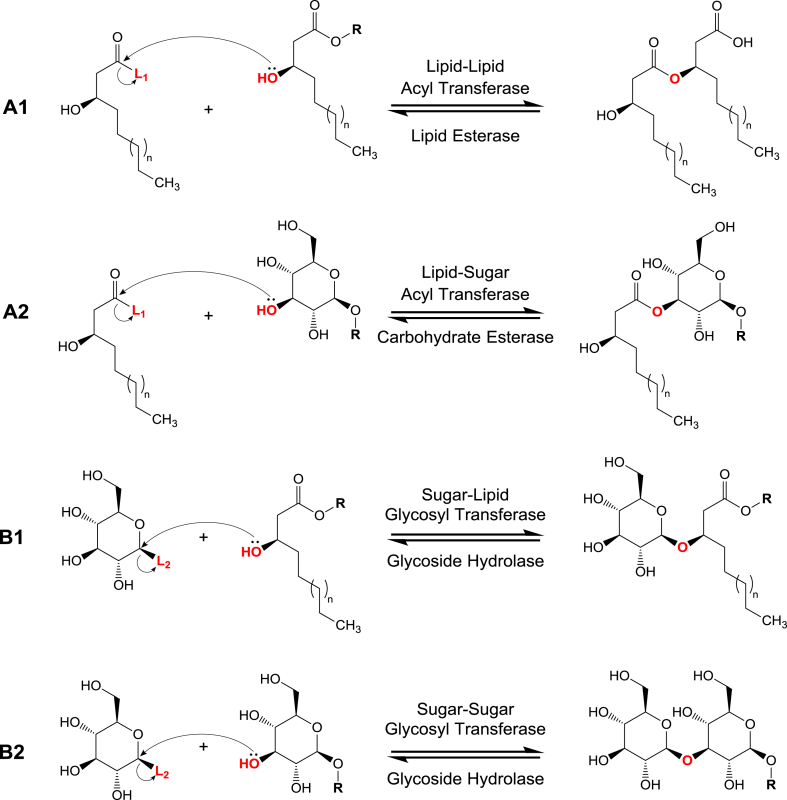
Fig. 4.
Key enzymes of glycolipid biosynthesis and hydrolysis. Last steps of glycolipid biosynthesis involves linking of sugar and lipid moieties via either or both Acyl Transferases (AT) (A1 and A2, forward reactions) and Glycosyl Transferases (GT) (B1 and B2, forward reactions) which catalyze the ester and glycosidic bonds formation, respectively. Glycolipids are catabolized or broken down by Lipid Esterase (LE), Carbohydrate Esterases (CE) and Glycoside Hydrolases (GH) that hydrolyze the bond between alkyl-alkanoate ester, acyl-sugar ester and glycosidic bonds, respectively (reverse reactions). L1: Coenzyme A (CoA-S-) or Acyl Carrier Protein (ACP-S-) activating groups on acyl donors; L2: Nucleotides or phosphates activating groups on glycosyl donors. R: any substitution that could be glycosyl, lipid, or glycolipid units. Notes: β-glucose and R-3-hydroxyalkanoate are used as examples of any sugar and hydroxyl fatty acid of any chain length (n), respectively. Hydrolysis reactions do not generate activated products.