Figure 5.
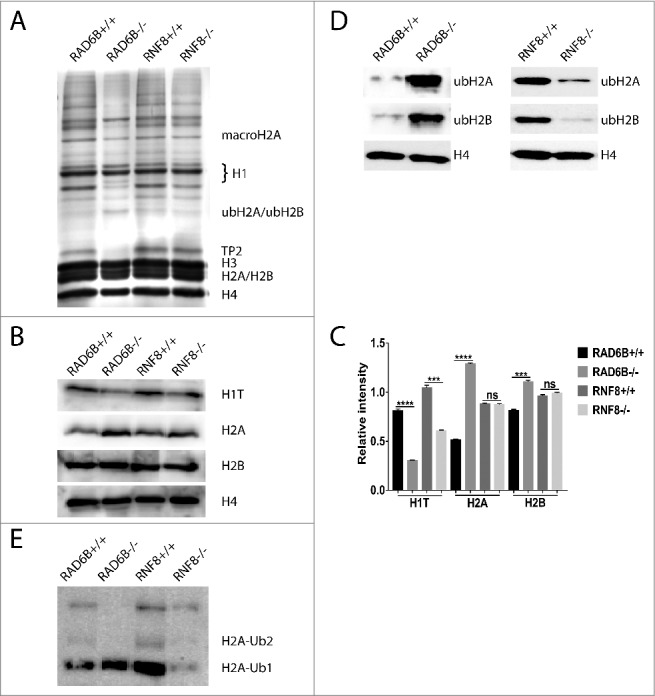
H2 (A)and H2B ubiquitination were increased in testes from RAD6B−/− males but decreased in testes from RNF8−/− males. (A) Basic nuclear proteins were isolated from total testis from WT, RNF8−/− and RAD6B−/− mice, separated using 15% SDS-PAGE, and stained with Coomassie blue. Proteins were excised from the gel and identified by MS. (B) H1 T was decreased in testes from RNF8−/− and RAD6B−/− mice and H2 A and H2B were increased in testes from RAD6B−/− males. In contrast, no significant changes were observed in RNF8−/− males. Western blots of proteins using testes from WT, RNF8−/− and RAD6B−/− mice are shown. Antibodies used are indicated, and H4 was used as a loading control. (C) The relative expression levels of H1 T, H2 A and H2B in panel B are summarized in the histogram (mean ± SEM). (D) ub-H2 A and ub-H2B were decreased in testes from RNF8−/− mice but increased in testes from RAD6B−/− mice. Western blots of proteins from testes of WT, RNF8−/− and RAD6B−/− mice are shown. Antibodies used are indicated, and H4 was used as a loading control. (E) H2 A-ub2 had almost completely disappeared from the testes of RAD6B−/− mice and was decreased significantly in the testes of RNF8−/− mice. Western blots of proteins using testes from WT, RNF8−/− and RAD6B−/− mice are shown.
