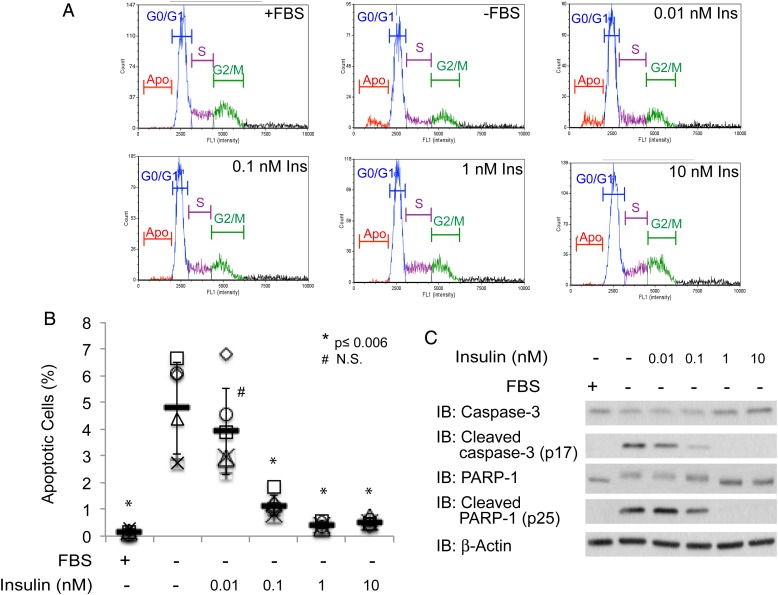
Fig. 1.
Insulin rescues CHO-IR cells from undergoing serum-withdrawal induced programmed cell death. (A) Distribution of fluorescence intensity of PI stained CHO-IR cells that were cultured in the presence or absence of serum and 0.01, 0.1, 1 and 10 nM insulin for 24 h. (B) Scatter plots represent the percentage of apoptotic cells from each condition (n = 6). Independent experiments were plotted with an identical symbol for different conditions. Black bars indicate the average percentage from six independent experiments, and the error bars indicate ± STDEV. Student's t-test (paired, one-tailed) was used to evaluate statistical significance using serum-deprived sample as the control. * P ≤ 0.006, # NS, not significant. (C) Western blots of apoptotic markers, cleaved caspase-3 and cleaved PARP-1. Antibodies against full-length caspase-3 and PARP-1, as well as β-actin, are included as controls. This figure is available in black and white in print and in colour at Glycobiology online.