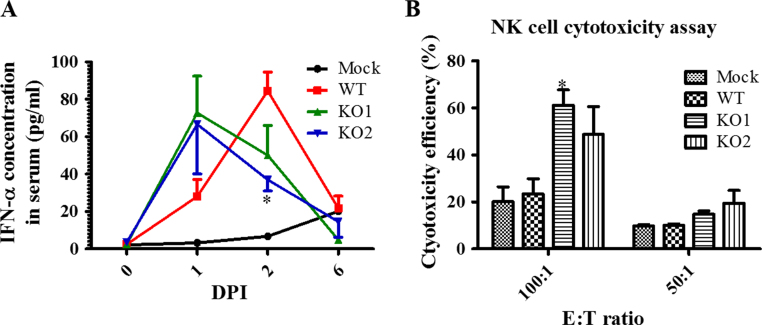
Fig. 7.
Comparison of IFN-α production levels and NK cell cytotoxicity in pigs inoculated with WT virus and nsp2TF/nsp2N-deficient mutants. Pigs were uninfected (mock) or infected with WT PRRSV (WT), vKO1 or vKO2 mutant. (A) IFN-α levels in serum samples collected at 0, 1, 2 and 6 DPI were analyzed with a ProcartaPlex Porcine IFN alpha Simplex kit. (B) PBMCs (NK effectors) harvested on the day of necropsy (6 DPI) were co-cultured with target cells (K562) at an E:T ratio of 100:1 or 50:1. After overnight incubation, flow cytometry was performed to evaluate the NK cell-specific cytotoxic activity. Each data point represents the mean value and SEM of data from 3 pigs. Statistical significance between the wild-type virus infected group and mutant virus-infected groups was determined by one-way ANOVA (Tukey's test) and indicated with asterisks (*, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001).