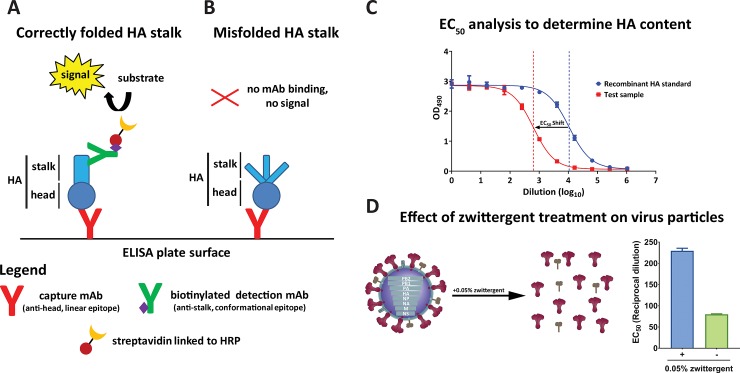
Fig 1. Development of capture ELISA to measure correctly folded HA stalk domain.
(A) and (B) describe the underlying concept of the assay. The assay was primarily developed to detect HA with conformationally intact stalk epitopes. The capture mAb in this assay recognizes the HA head linear epitope. On the other hand, the detection mAb recognizes the conformational epitope in the HA stalk. (A) If the stalk of the HA is properly folded, the detection mAb can bind and thus produces a signal. (B) If the stalk is misfolded, no signal is observed since the detection mAb cannot recognize the HA stalk. (C) HA concentration was calculated using a curve-fit model similar to parallel line analysis in which EC50 values are used to determine relative amounts. An EC50 analysis is shown using a recombinant protein standard with a known concentration for reference. The shift in EC50 between protein standard and test samples was then used to calculate the HA content of test samples. (D) The test samples were treated with 0.05% zwittergent for 1h to solubilize the influenza virus membrane and prevent transmembrane-driven rosette formation. EC50 values of virus preparations treated with or without zwittergent were calculated. Bars represent mean with error bars representing standard error of the mean.