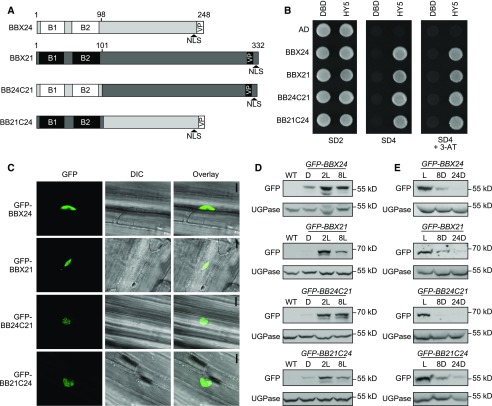
Figure 2.
BBX24/BBX21 chimeric proteins retain expected functions. A, Schematic presentation of full-length BBX24 and BBX21 proteins and the two chimeric versions. B, Yeast two-hybrid assay using HY5 as bait and BBX24, BBX21, BB24C21, and BB21C24 as prey. C, Nuclear localization of GFP-fused domain-swapped chimeric proteins in hypocotyl cells of 4-d-old dark grown seedlings exposed to 2 h of white light (scale bar, 10 μm). D, Immunoblot analysis of GFP-fusion proteins grown for 4 d in darkness (D) and exposed to 75 μmol m−2 s−1 white light for 2 h and 8 h. E, Immunoblot analysis of seedlings grown for 4 d in 75 μmol m−2 s−1 of white light and moved to darkness for 8 h and 24 h. Anti-GFP was used to detect GFP-BBX fusion proteins and anti-UGPase was used as a loading control. Wild type served as a negative control. B1, first B-box; B2, second B-box; SD2, media lacking Trp, Leu; SD4, media lacking Trp, Leu, His, Ura; 3-AT, addition of 1 μM 3-amino-1, 2,4-triazol to the growth media; L, light; 2L, white light for 2 h; 8L, white light for 8 h; 8D, dark for 8 h; 24D, dark for 24 h; WT, wild type.