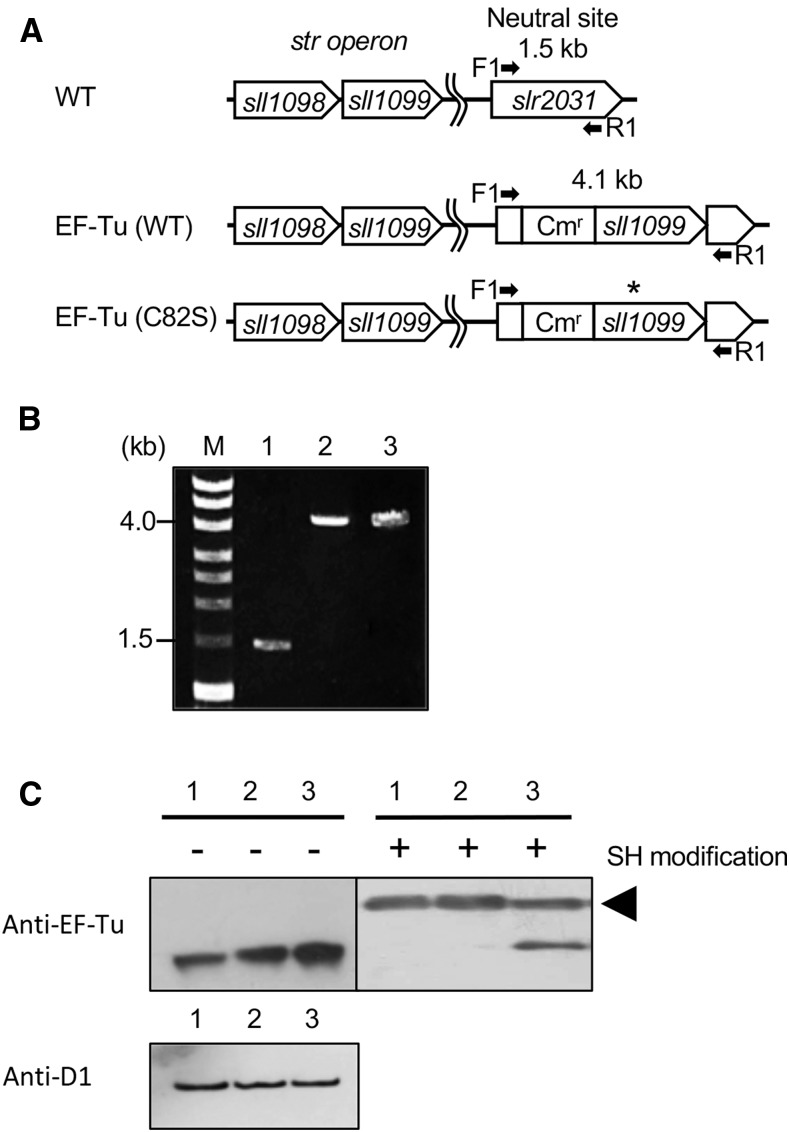
Figure 2.
Expression of mutated EF-Tu in Synechocystis. A, Schematic representation of the incorporation of the wild-type sll1099 gene for EF-Tu and its mutated derivative at a neutral site between slr2030 and slr2031 in the genome of Synechocystis. The asterisk indicates the position of site-directed mutagenesis for replacement of Cys-82 by a Ser residue. Arrows indicate the positions and directions of primers (F1 and R1) for PCR. B, Confirmation by PCR of the complete incorporation of the mutated sll1099 gene at the neutral site in all the chromosomal copies of the genome. Genomes from wild-type (lane 1), EF-Tu (wild type; lane 2), and EF-Tu (C82S; lane 3) cells were extracted and used as templates for PCR. C, Expression of wild-type and mutated EF-Tu in Synechocystis cells. Proteins in cell extracts from wild-type (lane 1), EF-Tu (wild type; lane 2), and EF-Tu (C82S; lane 3) cells were separated by reducing SDS-PAGE and also by nonreducing SDS-PAGE after modification of thiol groups with PEG-maleimide, and then EF-Tu was detected immunologically. The arrowhead indicates thiol-modified EF-Tu. As a control, levels of the D1 protein were detected immunologically. Cmr, chloramphenicol-resistance gene cassette; M, molecular mass markers; SH, thiol groups; WT, wild type.