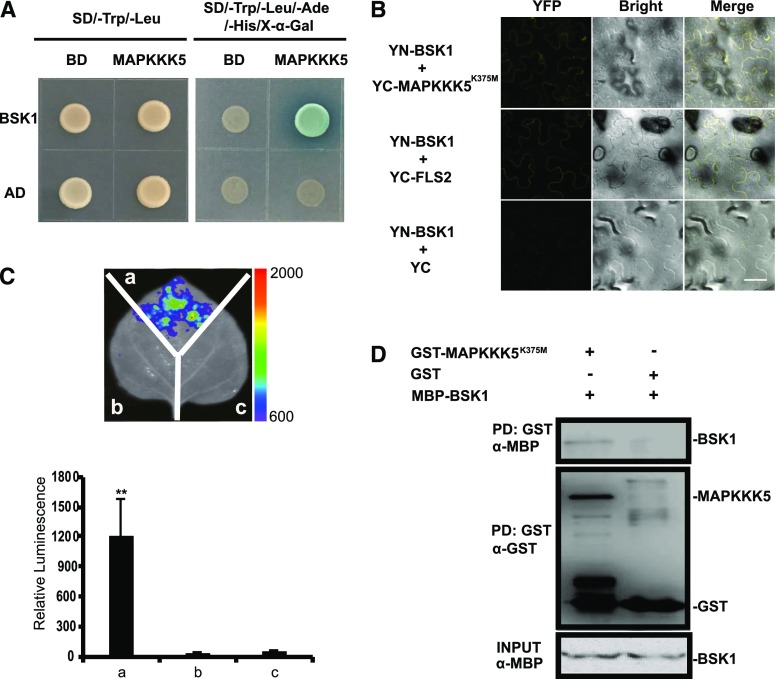
Figure 1.
MAPKKK5 interacts with BSK1. A, MAPKKK5 interacted with BSK1 in the yeast two-hybrid assay. Yeast cells containing the indicated plasmids were spotted onto the SD/-Trp/-Leu or SD/-Trp/-Leu/-Ade/-His/X-α-Gal medium, as indicated. Photos were taken after 3 d of incubation. B, The interaction between BSK1 and MAPKKK5 was examined with the BiFC assay in N. benthamiana. BSK1 and MAPKKK5K375M were fused to the N terminus or C terminus of the YFP fragment, respectively. YFP fluorescence was detected by confocal microscopy. Bar = 50 μm. The combination of YN-BSK1 and YC-FLS2 was used as the positive control. C, The interaction between BSK1 and MAPKKK5 was examined with the LUC assay. Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 containing the indicated construct pairs was coinfiltrated into N. benthamiana leaves. The infiltrated leaves were removed and sprayed with 1 mm luciferin and the fluorescence signal was captured by a CCD camera at 2 d after injection. Left panel, a, Cluc-BSK1 + MAPKKK5K375M-Nluc; b, empty vector (Cluc) + MAPKKK5K375M-Nluc; c, Cluc-BSK1 + empty vector (Nluc). The color bar at the right side of the left panel displays the relative luminescence units. Right panel, the relative luminescence unit in the histogram was measured 3 d after injection. Data represent mean ± sd. Two asterisks indicate statistically significant differences [n ≥ 8; P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA (ANOVA)]. D, The interaction between BSK1 and MAPKKK5 was examined with the in vitro pull-down assay. MBP-tag fused BSK1 protein was incubated with GST-bound beads and GST or GST-fused MAPKKK5K375M. Protein was detected by an immunoblot assay with α-GST or α-His antibodies, respectively. AD, pGADT7; BD, pGBKT7.