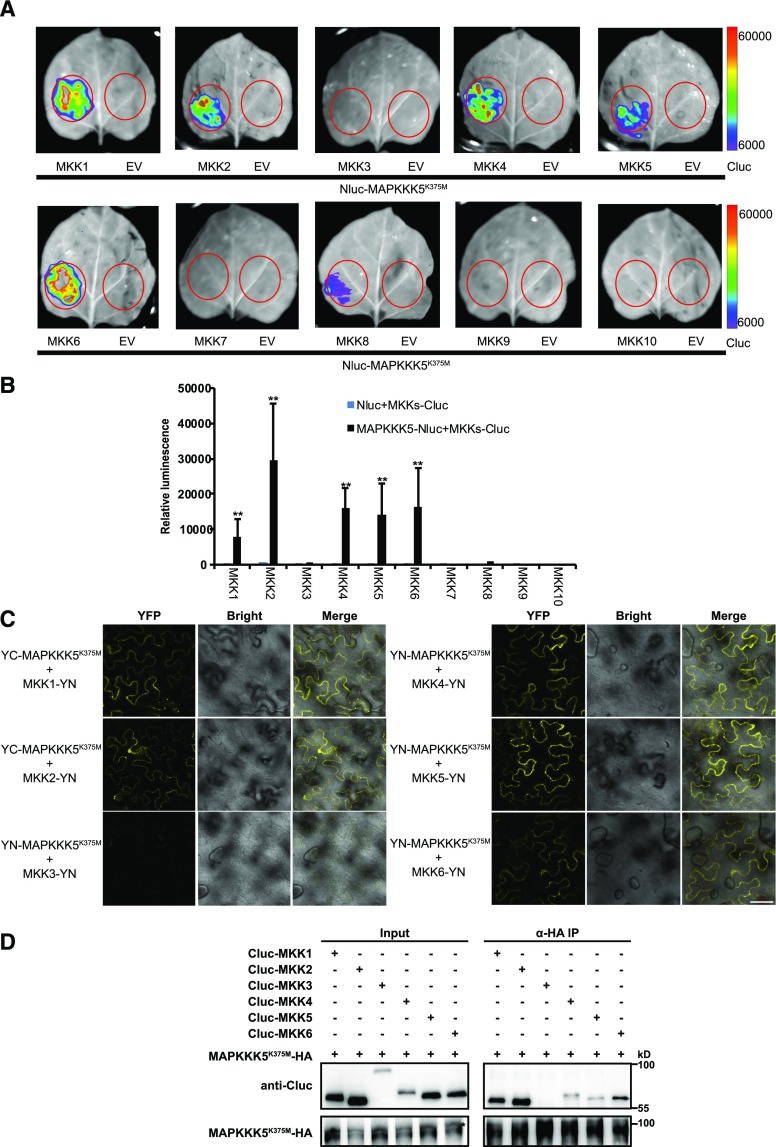
Figure 8.
MAPKKs interact with MAPKKK5. A, The interaction between 10 MKKs and MAPKKK5 was examined by the luciferase complementation imaging assay. MAPKKK5K375M and MKKs were fused to the N-terminal or C-terminal fragment of firefly luciferase. Bars on the right display the relative luminescence units. B, Quantitative analysis of the interaction of MAPKKK5 and MKKs in (A). Constructs were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves and the relative luminescence unit was measured 3 d after injection. Data represent mean ± sd. An empty vector was used as a control. Two asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (n ≥ 8; P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA). C, The interaction between MAPKKK5 and MKKs was examined with the BiFC assay in N. benthamiana. MAPKKK5K375M and MKKs were fused to the YN and YC, respectively. YFP signal was detected by confocal microscopy. Bar = 50 μm. D, MAPKKK5 interacted with MKK1/2/4/5/6 in Arabidopsis protoplasts. Co-IP of MKKs and MAPKKK5K375M from Arabidopsis protoplasts transiently expressing Cluc-MKK1/2/3/4/5/6 and MAPKKK5K375M-HA. The MAPKKK5K375M protein was immunoprecipitated by HA antibody, followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-Cluc antibody. Asterisk indicates MAPKKK5K375M-HA. EV, empty vector.