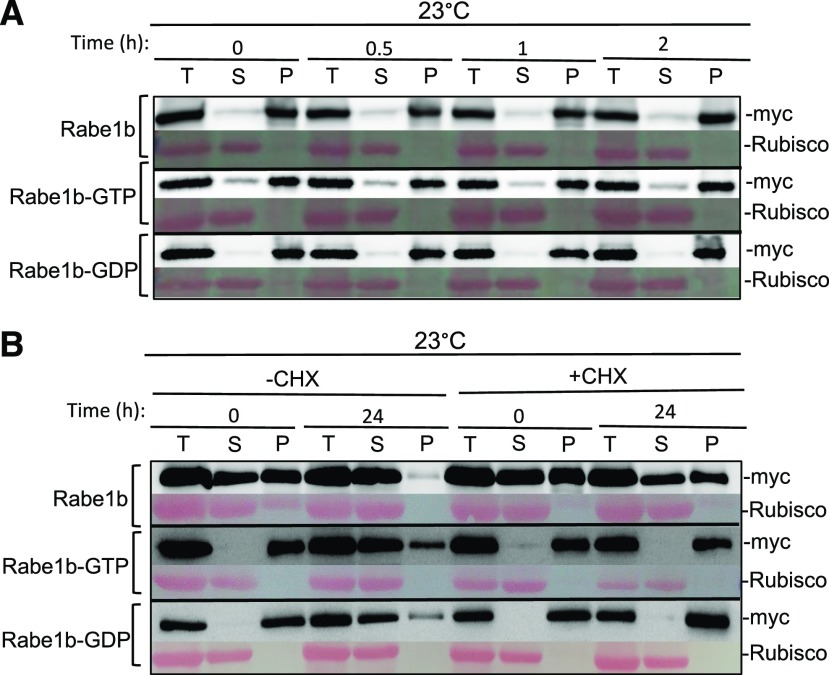
Figure 4.
Analysis of heat-induced Rabe1b aggregates during recovery. A, Heat-induced Rabe1b aggregates during recovery in vitro. Total proteins were extracted from transgenic AtRabe1b-OE, AtRabe1b-GTP-OE, and AtRabe1b-GDP-OE Arabidopsis plants incubated at 42°C for 2 h to induce Rabe1b aggregation and then placed at 23°C for the indicated hours. Total proteins (T), soluble proteins in the supernatants (S), and insoluble proteins in the pellets (P) were separated, and the amount of myc-tagged AtRabe1b proteins in the fractions was analyzed by immunoblotting. Rubisco proteins stained with Ponceau S are shown as the loading control. B, Effects of a protein synthesis inhibitor on heat-induced Rabe1b aggregates during recovery in vivo. Transgenic AtRabe1b-OE, AtRabe1b-GTP-OE, and AtRabe1b-GDP-OE Arabidopsis plants were treated with the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX; 100 μm) and then incubated at 45°C for 6 h. The plants were then transferred to 23°C for recovery. Total proteins were extracted from treated plants at 0 and 24 h of recovery. Soluble proteins in the supernatants and insoluble proteins in the pellets were separated, and myc-tagged AtRabe1b proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting. Rubisco proteins stained with Ponceau S are shown as the loading control.