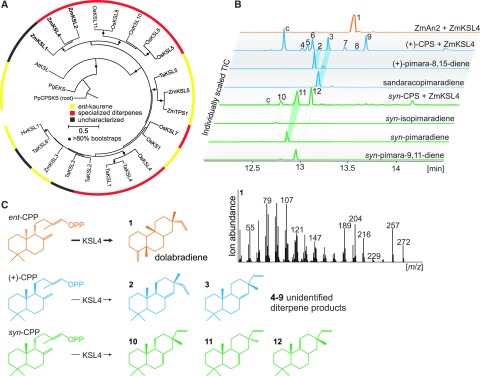
Figure 2.
Functional characterization of the maize diterpene synthase ZmKSL4. A, Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of select monocot class I diTPSs (Supplemental Table S2). The tree is rooted with the ancestral Physcomitrella patens ent-kaurene synthase. Circles indicate bootstrap support of greater than 80% (500 repetitions), and the functional association with the biosynthesis of ent-kaurene (yellow) or specialized diterpenoids (red) is highlighted. B, Total ion chromatograms (TIC) of reaction products resulting from E. coli coexpression assays of ZmKSL4 with ZmAN2 CPP synthase (Harris et al., 2005), rice CPS4 syn-CPP synthase (Xu et al., 2004), and the grand fir abietadiene synthase variant D621A producing (+)-CPP (Peters and Croteau, 2002) as compared with available authentic standards for product identification. Compound c represents a contamination product from the engineered E. coli system. C, Major products of ZmKSL4 from prenyl diphosphate intermediates of ent-, normal (+)-, and syn-stereochemistry. The mass spectrum of dolabradiene 1 resulting from the coupled activity of ZmAN2 and ZmKSL4 is shown, and the structure of dolabradiene is depicted as verified by NMR analysis.