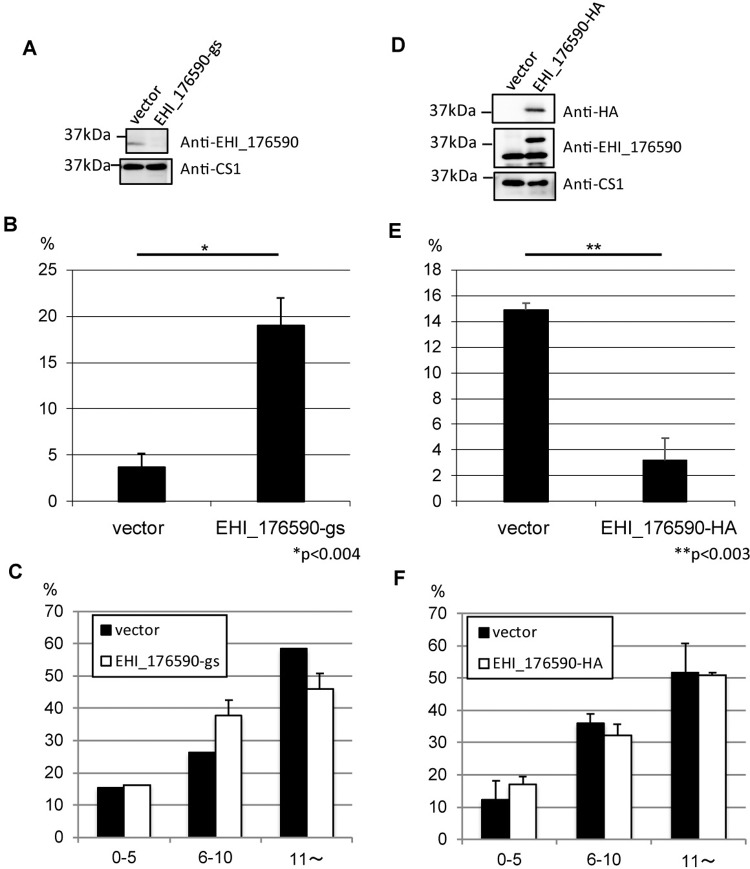
Fig 7. Liver abscess formation in hamsters challenged with EHI_176590 gene-silenced and EHI_176590-HA-expressing transformants using animal-passaged virulent strain Cl6.
(A) Confirmation of EHI_176590 gene silencing by immunoblot analysis. Total lysates, from EHI_176590 gene-silenced and mock transformants, were subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-EHI_176590 (upper panel) and control anti-CS1 antibodies (lower panel). (B) Effect of EHI_176590 gene silencing on liver abscess formation. Approximately 1×106 trophozoites of EHI_176590 gene-silenced and mock-transfected strains (created from animal-passaged virulent Cl6) were injected into the livers of hamsters. Injected animals were sacrificed 6 days post-infection, and the liver and abscesses were dissected and weighed separately. Averaged percentages of the weight of abscesses per liver are shown. *p<0.004. (C) Adhesion of EHI_176590 gene-silenced and mock-transfected strains to HRBCs. Mock-transfected (black bars) and EHI_176590 gene-silenced (white bars) strains were co-cultured with HRBCs on ice for 30 min, and adherent HRBCs per ameba were counted. The percentage of trophozoites, bound to 0–5, 6–10, or >10 HRBCs, are shown. Error bars indicate standard deviations of three biological replicates. (D) Confirmation of EHI_176590-HA expression by immunoblot analysis. Total lysates from EHI_176590-HA and mock transformants were analyzed by immunoblot with anti-HA, anti-EHI_176590, and anti-CS1 antibodies (upper, middle, and lower panels, respectively). (E) Effect of EHI_176590-HA overexpression on liver abscess formation. Approximately 3×106 trophozoites, of EHI_176590-HA and mock-transfected transformants, were injected into the liver of hamsters, and liver abscess formation was evaluated as in (B). **p<0.003. (F) Adhesion of EHI_176590-HA and mock-transfected strains to HRBCs. Trophozoites of mock-transfected (black bars) and EHI_176590-HA transfected (white bars) strains were co-cultured with HRBCs, and adhesion was evaluated as in (C).