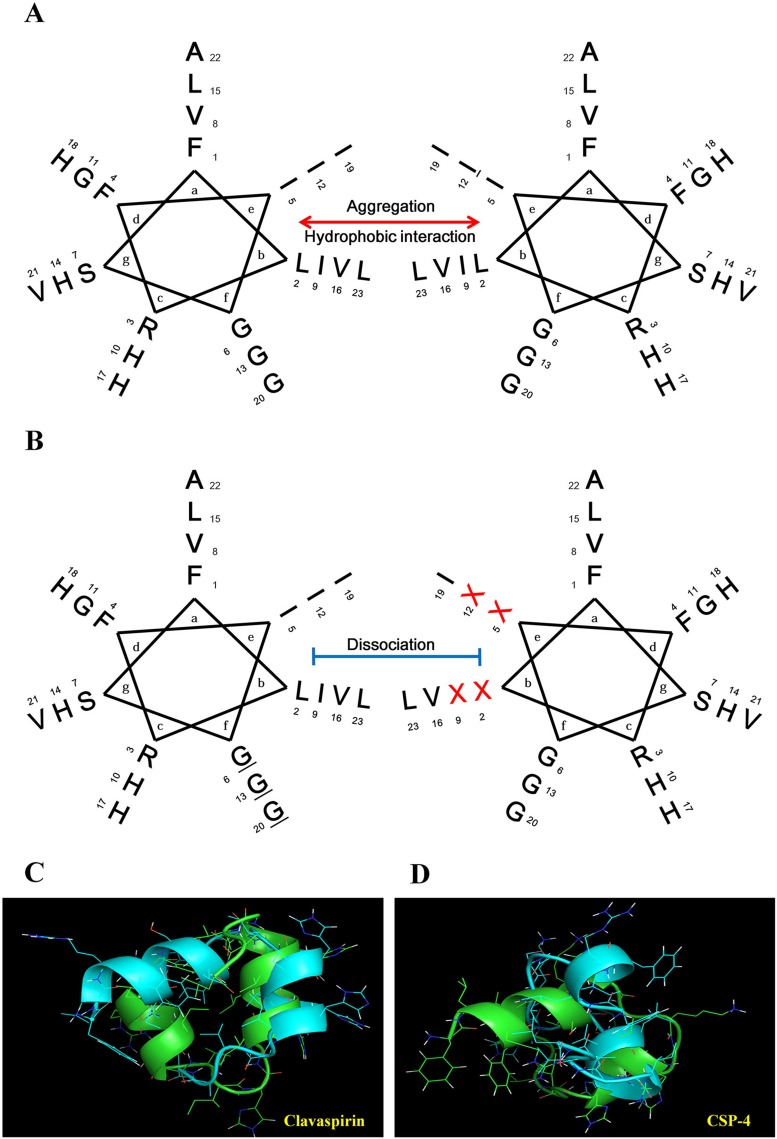
Figure 1. Helical wheel diagram structure of the clavaspirin peptide (CSP) and its analogs.
(A) CSP possesses a 310-helical structure (coiled-coil) and a leucine-zipper motif. The residue positions are labeled from a to g. Hydrophobic interactions between amino acid residues in positions e and b appear in the helical wheel diagram structure. (B) Isoleucine and leucine residues at positions 2, 5, 9, and 12 are located in the same face, allowing for the formation of a leucine-zipper. Analogue peptides were designed by substitution of the X position amino acid. We designed 4 peptide analogs by substituting the hydrophobic amino acids (CSP-1, I5A, and I12A; CSP-2, I5K, and I12K; CSP-3, L2K, and I9K; and CSP-4, I9K, and I12K) in the leucine-zipper motif. The resulting analogs were named CSP-1, CSP-2, CSP-3, and CSP-4. Peptide structure analysis was conducted using the PEP-FOLD program (http://bioserv.rpbs.univ-paris-diderot.fr/services/PEP-FOLD/). (C) CSP showed peptide-peptide interactions as in a leucine zipper motif. (D) CSP-4 structure showed disruption of the repeat leucine and/or isoleucine zipper motif.