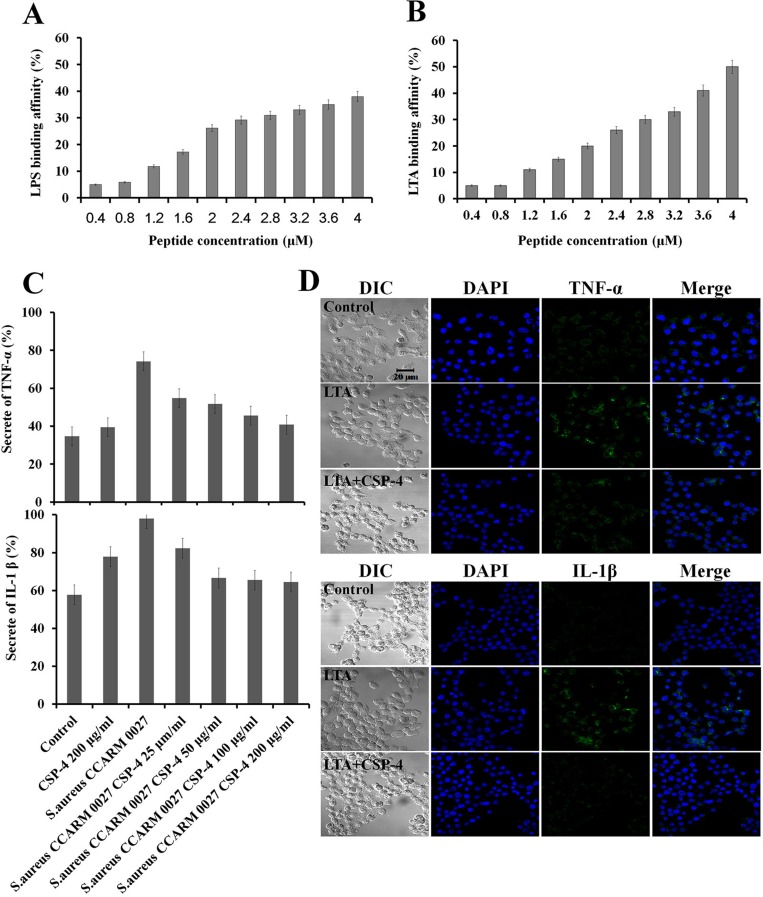
Figure 3. Binding of CSP-4 to LPS and LTA and CSP-4-induced inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines in RAW 264.7 macrophages.
(A, B) CSP-4 binding at the indicated concentrations to E. coli LPS in 5 mM HEPES buffer, as measured using 2.5 μM dansyl polymyxin B (Ex. 340 nm, Em. 485 nm). All values represent the mean ± SD of three individual experiments (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). (C) Secretion of TNF-α (top) and IL-1β (bottom) from RAW 264.7 cells exposed to S. aureus CCARM 0027 (1 × 106 cfu/mL) and subsequently treated with CSP-4 (25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/mL). All values represent the mean ± SD of three individual experiments (p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA). (D) The effect of CSP-4 (100 µg/mL) on S. aureus LTA-induced expression of TNF-α and IL-1β in RAW 264.7 macrophages. The cells were stimulated with LTA (1 µg/mL) for 3 h in the presence and/or absence of CSP-4 at pH 5.5 (top) or pH 7.4 (bottom), fixed, permeabilized, and stained with antibodies. Scale bar, 20 μm.