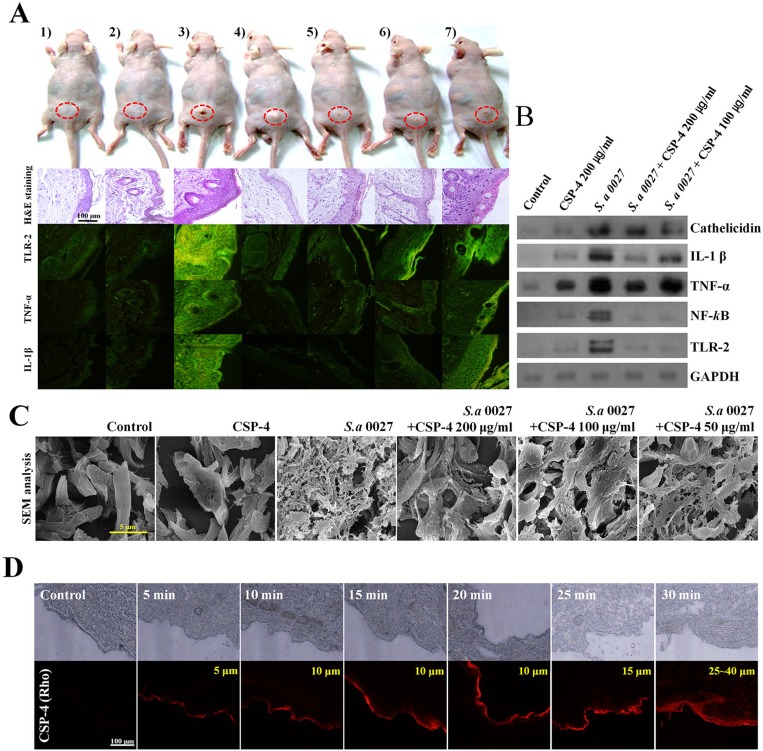
Figure 4. Application of CSP-4 to hairless mouse skin.
(A) Hairless mouse skin infected with S. aureus CCARM 0027 (1 × 108 cfu/mL) leading to dermatitis. Mice were treated topically with 200, 100, 50, or 25 µg/mL CSP-4 and were sacrificed 7 days later. Dorsal skin tissue was collected and stained using hematoxylin and eosin or FITC-conjugated anti-TLR-2, anti-TNF-α and anti-IL-1β antibodies, as indicated. From left to right, samples were treated with 1) PBS, 2) 200 µg/mL CSP-4, 3) S. aureus CCARM 0027 at 1 × 108 cfu/mL, 4) S. aureus and 200 µg/mL CSP-4, 5) S. aureus and 100 µg/mL CSP-4, 6) S. aureus and 50 µg/mL CSP-4, and 7) S. aureus and 25 µg/mL CSP-4. Scale bar, 100 μm. (B) Western blots showing the effect of CSP-4 on S. aureus CCARM 0027-induced expression of the indicated pro-inflammatory signaling proteins and AMP cathelicidin. (C) Scanning electron micrographs showing morphological changes in the dermis of the hairless mouse under the indicated conditions. S. aureus CCARM 0027 was added at 1 × 108 cfu/mL. Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Time-dependent penetration of hairless mouse skin by rhodamine-labeled CSP-4 (red; 200 μg/mL). Scale bars, 100 µm. Numbers in the upper right of the fluorescence micrographs indicate depth of penetration.