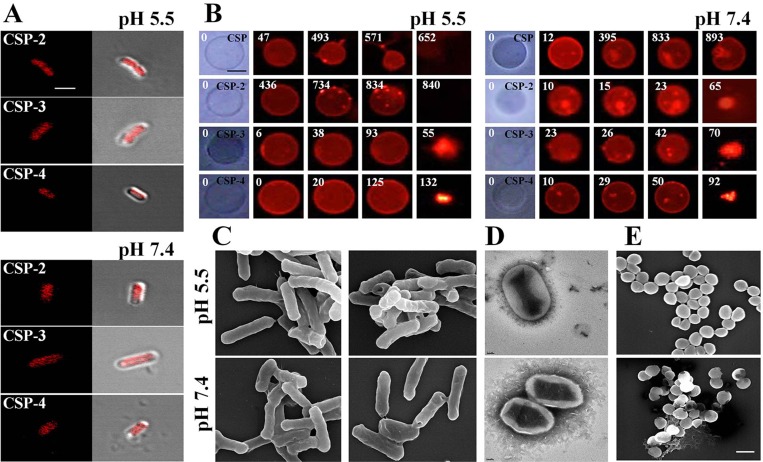
Figure 7. Accumulation of CSP and its analogues on the bacterial cell membrane.
(A) Localization of the indicated CSP analogues on E. coli. Cells were incubated for 20 min with the MICs of rhodamine-labeled AMPs. Cells were visualized using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Scale bar, 5 μm. (B) Effect of CSP (20 μM; pH 5.5 or pH 7.4) and the indicated CSP analogues on GUVs (PE/PG/PE-rhodamine). Scale bar, 50 μm. Scanning (C, E) and transmission (D) electron micrographs show disruption of the E. coli and S. aureus cell membrane by CSP-4 at 1/2 MIC in 10 mM sodium phosphate buffer (pH 5.5 and pH 7.4). The panels show formation of large pores after exposure to CSP-4. S. aureus cells were cultured in the absence (top) and presence (bottom) of CSP-4. Scale bar in C and E, 5 µm; scale bar in d, 2 nm.