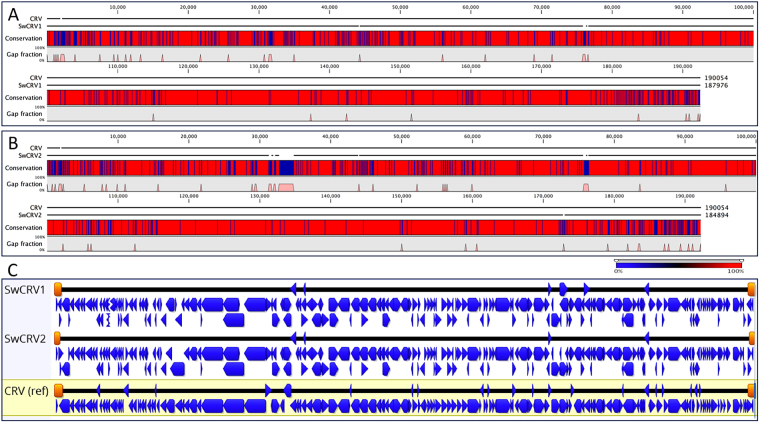
Figure 2.
Comparative genome architectures of the SwCRV-1 and -2. (A) Sequence alignment of saltwater crocodilepox virus subtype 1 (SwCRV-1, GenBank accession number MG450915) to the reference Nile crocodilepox virus (CRV, DQ356948) genome. (B) Sequence alignment of saltwater crocodilepox virus subtype 2 (SwCRV-2, GenBank accession number MG450916) to the reference Nile crocodilepox virus (CRV, DQ356948) genome. The alignment was performed using the global alignment program contained in CLC Genomic Workbench (tool for Classical sequence analysis). The middle graphs in A and B represent the sequence conservation between the aligned SwCRV and CRV sequences at a given coordinate on the base sequence. The bottom graphs in A and B represent the gap fractions which are mostly for insertion and deletion between two representative viral genomes. (C) A sequence alignment using MAFFT in Geneious (version 10.2.3), and comparative ORF map of SwCRV and CRV. Protein coding ORFs, with blue arrows depicting the direction of transcription, whereas the orange blocks depicted Inverted Terminal Repeats (ITRs), respectively.