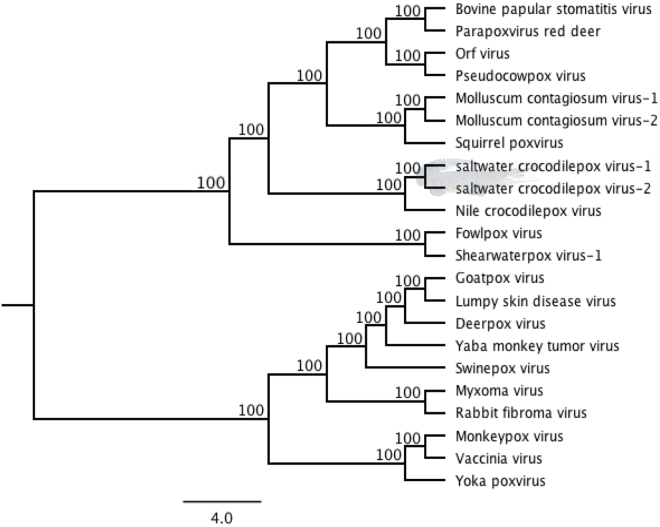
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree among selected complete genome sequences of poxviruses. The ML tree was constructed from a multiple-nucleotide alignment from the selected complete genome sequences of poxviruses. The numbers on the left show bootstrap values as percentages, and the clade consisted with SwCRV was highlighted using saltwater crocodile shading (taken and supplied by author S.R.I.). The GenBank accession details for poxviruses were used: CRV (Nile crocodilepox virus, DQ356948); MOCV1 (Molluscum contagiosum virus subtype 1, MCU60315); MOCV2 (Molluscum contagiosum virus subtype 2, KY040274); SQPV (Squirrel poxvirus, HE601899); BPSV (Bovine papular stomatitis virus, KM875470); PPRD (Parapoxvirus red deer, KM502564); ORFV (Orf virus, DQ184476); PCPV (Pseudocowpox virus, GQ329670); SwCRV-1 (saltwater crocodilepox virus subtype 1, MG450915); SwCRV-2 (saltwater crocodilepox virus subtype 2, MG450916); DPV (Deerpox virus, AY689436); GPV (Goatpox virus, KC951854); MYXV (Myxoma virus, KP723391); RFV (Rabbit fibroma virus, AF170722); LSDV (Lumpy skin disease virus, NC_003027); FWPV (Fowlpox virus, AF198100); SWPV-1 (Shearwaterpox virus-1, KX857216); YMTV (Yaba monkey tumor virus, NC_005179); MPXV (Monkeypox virus, JX878407); VACV (Vaccinia virus, AY678275); YKPV (Yoka poxvirus, HQ849551); SWPV (Swinepox virus, NC_003389).