Fig. 4.
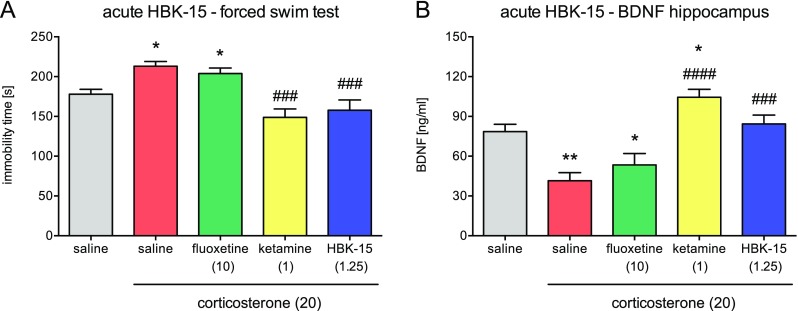
Effect of a single administration of HBK-15, fluoxetine, and ketamine on the immobility in the forced swim test (a) and BDNF level in the hippocampus (b) in corticosterone-treated mice. Corticosterone (20 mg/kg) was injected subcutaneously (s.c.) to mice for 3 weeks at random times during the light phase. Thirty minutes before the experiment, mice were intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with HBK-15 (1.25), ketamine (1 mg/kg), fluoxetine (10 mg/kg), or 0.9% NaCl (saline). Control group, which was injected for 21 days with saline containing 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and 0.1% Tween-80 (vehicle, s.c.), received saline (i.p.). Statistical analysis: one-way ANOVA (Newman–Keuls post hoc); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs control (non-corticosterone-treated) (saline, gray); ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001 vs corticosterone-treated control (saline, red); n = 8 mice per group (animal studies), n = 7 mice per group (biochemical studies) BDNF - brain-derived neurotrophic factor
