Fig. 1.
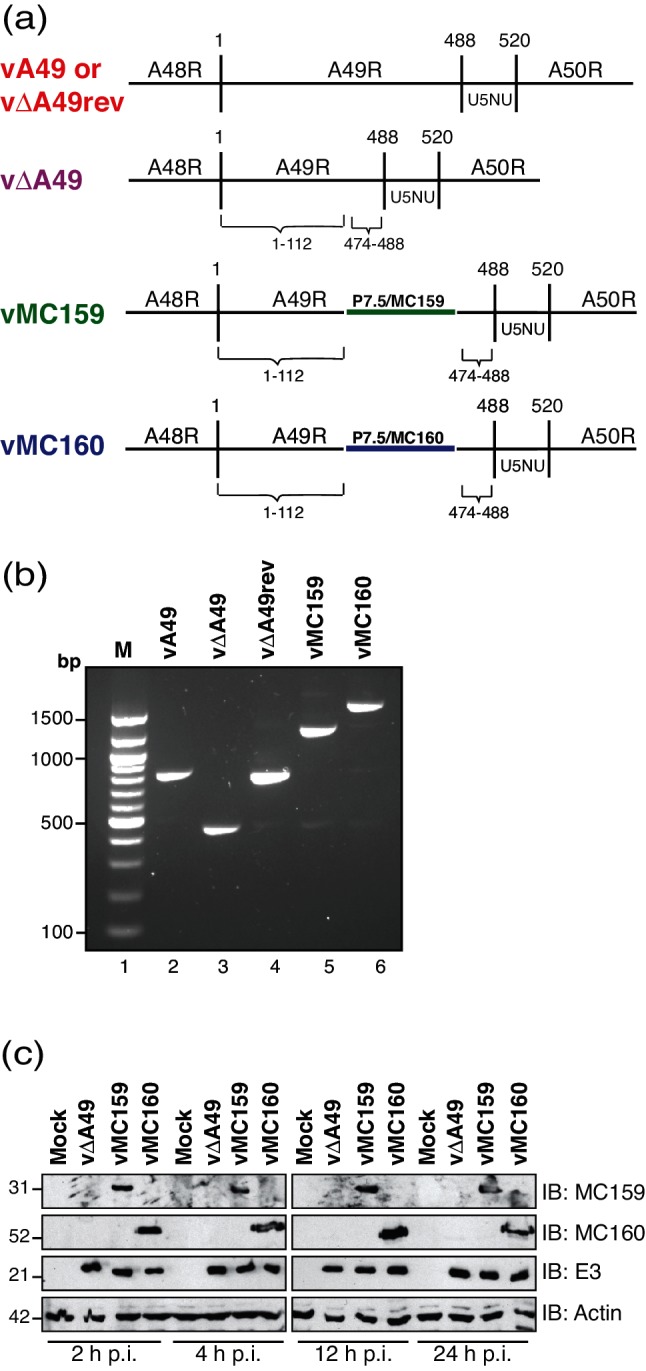
Characterization of vaccinia viruses expressing either MC159 or MC160. (a) A schematic of the viruses used in this study, focusing on the portion of the VACV WR genome containing the A49R gene and portions of the A48R and A50R genes flanking A49R. vΔA49 is a VACV strain in which A49R nucleotides 113–473 are deleted. Either the MCV MC159L or the MC160L genes, each under the control of the VACV p7.5 promoter, were inserted into vΔA49 to create vMC159 or vMC160, respectively. U5NU is the early gene transcription termination signal. (b) BSC40 monolayers were either mock-infected or infected with the indicated viruses (m.o.i.=10). At 24 h p.i., cells were collected and DNA was isolated. The DNA was PCR-amplified using a forward primer specific for A48R and a reverse primer specific for A50R [22]. A portion of each PCR reaction was analysed by gel electrophoresis. Bands were detected by ethidium bromide staining of the gel. (c) BSC40 monolayers were either mock-infected or infected with vΔA49, vMC159 or vMC160 (m.o.i.=10). Cells were lysed at the indicated times and 15 µg of clarified cellular lysates was subjected to immunoblotting for the presence of MCV (MC159 or MC160) or VACV (E3) proteins or cellular β-actin.
