Table 2. Potential mutations contributing to polymyxin resistance and acquired resistance genes.
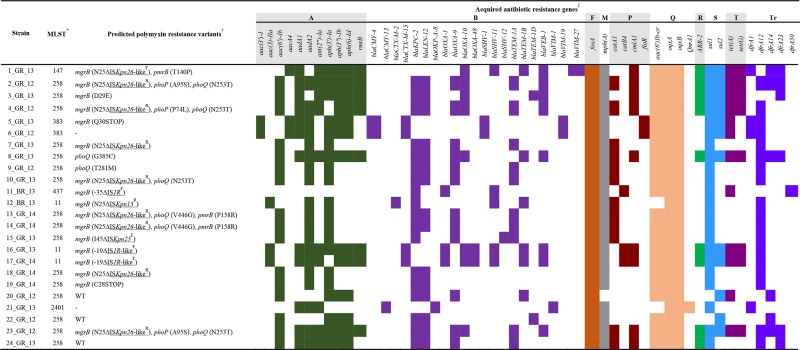 |
*Multilocus sequence type as identified through MultiLocus Sequence Typing Server 1.8.
†Variations detected in mgrB, phoPQ and pmrAB potentially causing polymyxin resistance. Significant non-synonymous changes determined by PROVEAN analysis. WT (wild-type) alleles in comparison to 20_GR_12. Displayed as gene impacted, initial amino acid, position and new amino acid. If a dash (–) is shown in front of the position, variant is encoded upstream and if a dash (–) is only displayed, no significant non-synonymous changes were detected in these loci. Insertion sequences (underlined) classified as Δ, identity as per ISFinder and orientation in superscript. Orientation determined as forward, F, if transposase is in the same direction as mgrB and conversely, reverse, R, if in the opposite direction to mgrB.
‡Acquired antibiotic resistance genes detected via ResFinder 3.0. Classes of antibiotics impacted are displayed as: A, aminoglycoside; B, beta-lactam; F; fosfomycin; M, macrolide; P, phenicol; Q, quinolone; R, rifampicin; S, sulphonamide; T, tetracycline; Tr, trimethoprim. Shading indicates detection of a gene (≥90 % homology, ≥60 % sequence length).
