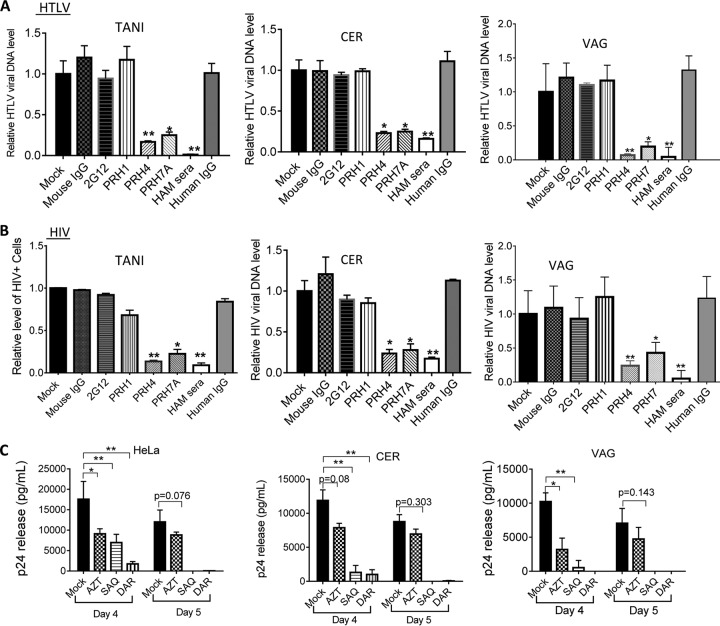
FIG 4 .
Infection with HTLV-1-pseudotyped HIV-1 was strongly inhibited by HTLV-1 neutralizing antibodies and HIV-1 inhibitor treatments. (A, B) TANI or primary VAG or CER epithelial cells were cocultured with HIV-1 IIIB–HTLV-1-coinfected T cells in the presence of antibodies as indicated. (A) De novo HTLV-1 DNA from infected TANI, CER, and VAG primary epithelial cells at day 5 postinfection was quantified by qPCR (normalized to the GAPDH internal control). (B) The effect of the antibodies on HIV-1 infection of epithelial cells was determined either by quantifying GFP-positive cells (TANI) or by quantifying the de novo level of HIV-1 DNA normalized to the GAPDH internal control (CER and VAG epithelial cells). PRH4 and PRH7A, neutralizing MAbs against HTLV-1 gp46; PRH1, HTLV-1 gp46 binding antibody without neutralizing activity; HAM serum, IgG from the serum of patients with HAM; 2G12, neutralizing MAb against HIV-1 gp120. Viral replication in mock-treated epithelial cells was set as 1.0. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.001. For PRH4 and PRH7A, data were compared to mouse IgG-treated samples. For HAM serum, data were compared to normal human IgG-treated samples. The data represent the mean ± the standard deviation of data from three independent experiments. The concentration used for PHR4, PRH7A, PRH1, and mouse IgG was 10 µg/ml. The concentration used for HAM serum IgG and normal human IgG was 100 µg/ml. The concentration used for 2G12 was 16 µg/ml. (C) HeLa cells and primary CER and VAG epithelial cells and were infected with HIV-1 by coculture with HIV-1 IIIB–HTLV-1-coinfected CD4+ T cells in the presence of AZT (10 µM), SAQ (0.4 µM), or DAR (0.5 µM). HIV-1 release into culture supernatants of epithelial cells was determined by p24 ELISA at days 4 and 5 postinfection. The data represent the mean ± the standard deviation of data from three independent experiments.