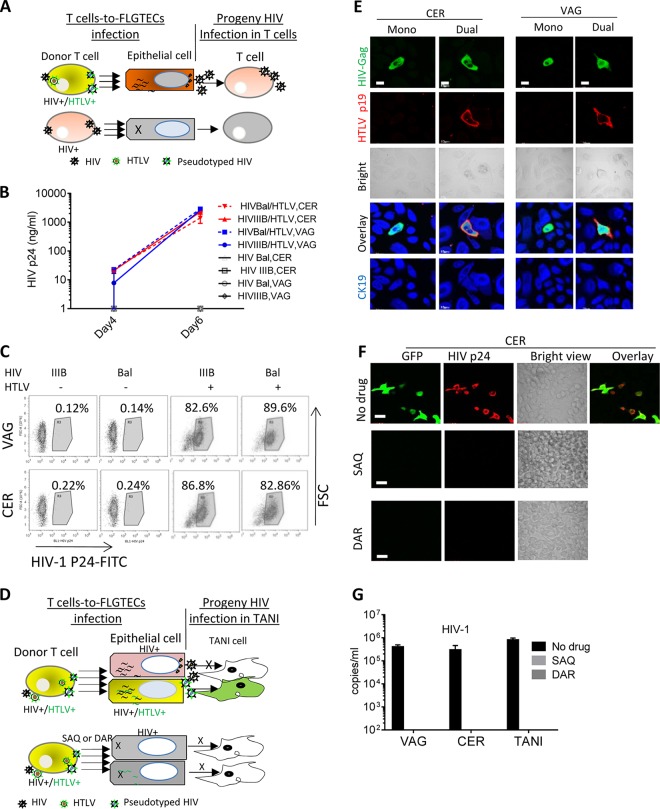
FIG 5 .
Genital epithelial cells infected with HIV-1 from HTLV-1-coinfected T cells efficiently transmit HIV-1 to susceptible T cells and also produce pseudotyped HIV-1. (A) Cartoon illustrating the system used to test the ability of primary epithelial cells HIV-1 infected through pseudotyping to produce infectious HIV-1. (B, C) The progeny virus from epithelial cells infected by coculture with infected T cells was added to naive PM1 cells. The viruses used to infect donor T cells and types of epithelial cells are as indicated. HIV-1 infection of PM1 cells was determined at days 4 and 6 postinfection by measuring HIV-1 release by p24 Gag ELISA (B) and at day 6 postexposure by quantifying HIV-1 p24 Gag-positive cells by flow cytometry (C). (D) Cartoon illustrating the system used to test whether HIV-1–HTLV-1-coinfected donor T cells can transmit both HIV-1 and HTLV-1 to epithelial cells, resulting in subsequent rounds of epithelial cell infection with pseudotyped HIV-1. SAQ and DAR should inhibit pseudotyped HIV-1 infection of epithelial cells and subsequent pseudotyped HIV-1 production. (E) HIV-1–HTLV-1-coinfected T cells transmitted both HIV-1 and HTLV-1 to epithelial cells. CER and VAG epithelial cells were infected by coculture with HIV-1 IIIB–HTLV-1-infected T cells and stained at day 5 postinfection for HIV-1 Gag (green), HTLV-1 p19 (red), and CK19. Mono, HIV-1 monoinfection; dual, HIV-1–HTLV-1 coinfection. Scale bars, 20 µm. (F, G) Epithelial cells were cocultured with HIV-1 IIIB–HTLV-1-coinfected T cells with or without the drugs indicated. Progeny HIV-1 from epithelial cells was added to TANI cells. (F) Images showing HIV-1 infection of TANI cells after exposure to progeny virus from infected CER cells as determined by analyzing GFP (green) and HIV-1 Gag expression (red). Scale bars, 20 µm. (G) HIV-1 release in culture supernatants from infected TANI cells at day 5 postexposure determined by qRT-PCR. The data represent the mean ± the standard deviation from three independent experiments.