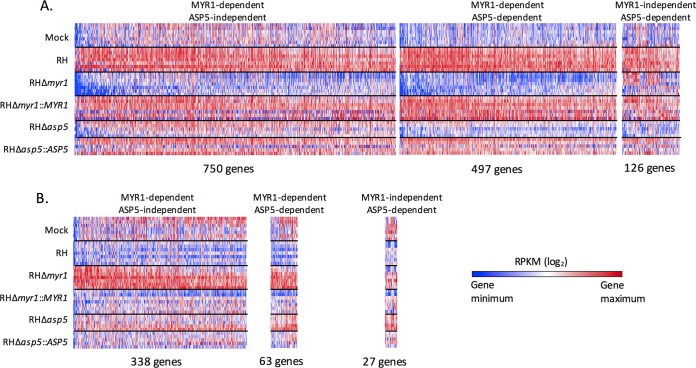
FIG 3 .
Comparison of genes differentially expressed in a MYR1- and ASP5-dependent manner compared to wild-type infection. Host gene responses are shown that are statistically significantly increased ≥1.5-fold (A) or decreased ≥1.5-fold (B) in cells infected with wild-type RH compared to RHΔmyr1 or RHΔasp5. Genes are considered MYR1- or ASP5-dependent if their change between RH and the respective knockout met the threshold of a q value of <0.05, 10% FDR, and ≥1.5-fold change, and were considered independent of these two parasite proteins if the differential gene expression did not meet that threshold. The first panel shows all genes that were significantly different in RHΔmyr1- but not RHΔasp5-infected cells relative to RH-WT infection, the middle panel shows genes that were different in both mutants relative to RH-WT, and the third panel shows genes that were different in only the RHΔasp5-infected cells (not RHΔmyr1 infections) relative to RH-WT. Genes in the first two panels are arranged from left to right in decreasing magnitude of difference between RH-WT- and RHΔmyr1-infected cells, and genes in the third panel are arranged in decreasing magnitude of the difference between RH-WT and RHΔasp5 infection. (C) MYR1-dependent and ASP5-dependent host genes were analyzed by GSEA, and the gene sets are displayed with a threshold of an FDR q value of <10−2. Complete lists of the genes contributing to the GSEAs shown for up- and downregulation are given in Tables S6 and S7, respectively. All other details are as in Fig. 2. (D) RPKM expression values of the EGR1 (early growth response 1) gene of HFFs infected with the indicated parasite lines. Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).