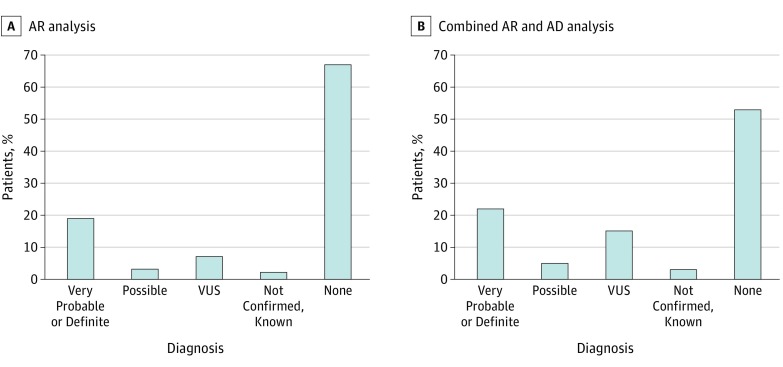
Figure 1. General Study Results.
Variants were sorted based on classic criteria (detailed in the Variant Analysis subsection of the Results section), then analyzed assuming an autosomal recessive (AR) transmission mode (including homozygous and heterozygous compound variants), which allowed identifying possibly to definitely causative variants in 74 patients (23.2%). Combining this analysis with one based on presumed autosomal dominant (AD) transmission (including heterozygous varients and a frequency ≤0.1%) improved this number to 91 patients (28.5%) for AD and AR inheritance modes, with 10 additional patients carrying very probable to definite pathogenic mutations. VUS indicates variant of unknown significance.