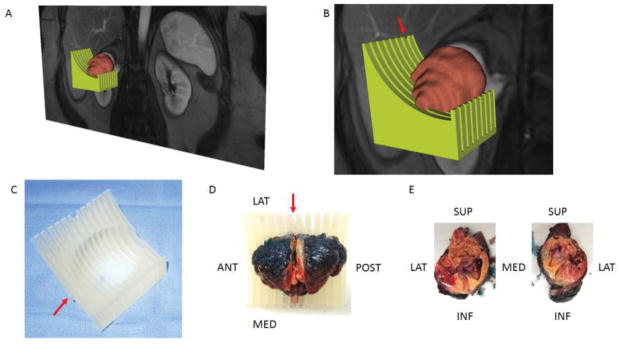
Figure 1.
A 3D object was generated by the model maker module in 3D Slicer and saved in the standard tessellation language (STL) file format. (A) The green-colored and brown-colored objects represent the STLs for the mold and tumor, respectively. (B) Zoomed-in image illustrating the notch in the mold (arrow) corresponding to the location of the preselected MRI image plane for radiomic analysis. (C) Printed mold using 3D printer with labeling on the anterior side (arrow). (D) Slicing of tumor positioned within the 3D mold at the level of the notch (arrow). (E) Tumor specimen after sectioning is positioned anatomically. Tissue samples can then be obtained from specific co-localized areas to the MRI findings.