Figure 3.
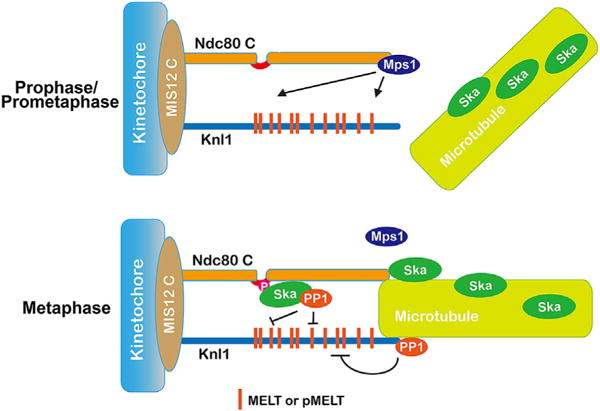
Stabilizing kinetochore-microtubule interactions and silencing the spindle checkpoint by the Ska complex. In prophase/prometaphase when kinetochores are poorly attached by microtubules, the kinetochore-localized Mps1 phosphorylates the MELT domains in Knl1 to recruit downstream effectors, thus activating the spindle checkpoint. At metaphase, microtubule attachments to kinetochores displace Mps1 from kinetochores and the kinetochore-microtubule attachments are stabilized by the Ska complex recruited by the Ndc80 N-terminus. At the same time, multiple copies of phospho (p)-MELT domains distributed along a wide range of amino-acid sequences in Knl1 are dephosphorylated by both the Ndc80-loop pool of Ska-PP1 and the Knl1-based PP1. The Ndc80-loop pool might provide extra dephosphorylating strength to more efficiently remove the phosphorylation from the phospho-MELT domains.
