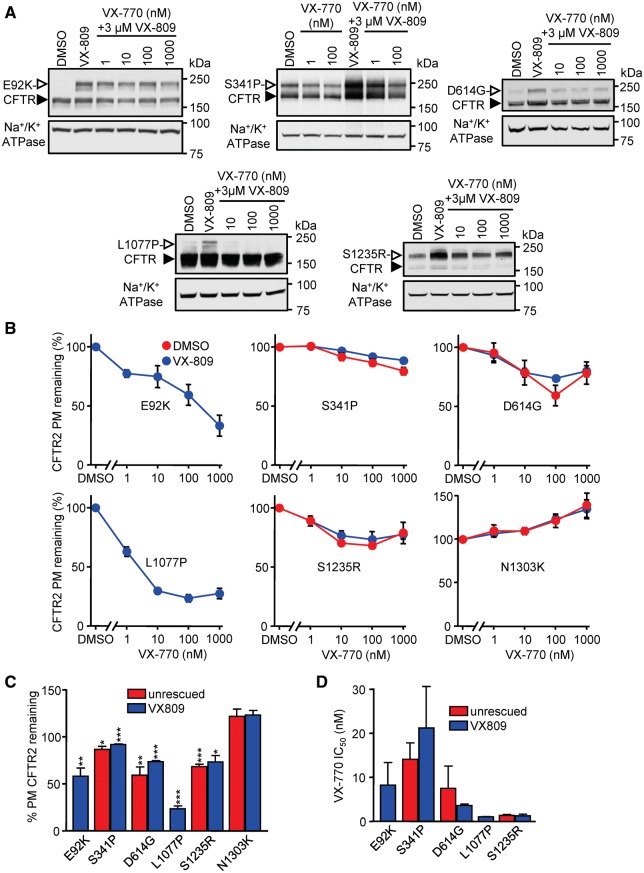
Figure 4.
Extended exposure to VX-770 leads to downregulation of a subset of CFTR mutants in a dose-dependent manner. (A) CFBE cells expressing the indicated CFTR mutants were incubated for 24 h with VX-809 (3 μM) and increasing concentrations of VX-770 and subsequently lysed to collect protein samples. Protein was detected by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. Na+/K+ ATPase was used as loading control. The empty arrowheads show the mature, complex glycosylated CFTR protein (C-band), and the filled arrowhead show the immature, core glycosylated protein (B-band). (B) PM density of CFTR2 mutants expressed in CFBE cells. Cells were treated with VX-770 for 24 h in the presence or absence of 3 µM VX-809, and the values, normalized with cell viability, are expressed as percentage of non–VX-770-treated controls (n = 3). (C) Quantification of remaining CFTR2 PM density, shown in B, after chronic treatment with 100 nM VX-770, as percent of DMSO control. Half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of VX-770 on PM expression of CFTR2 mutants, calculated on the basis of the measurements shown in panel B. Experiments in B, C and D are n = 3; error bars are SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.