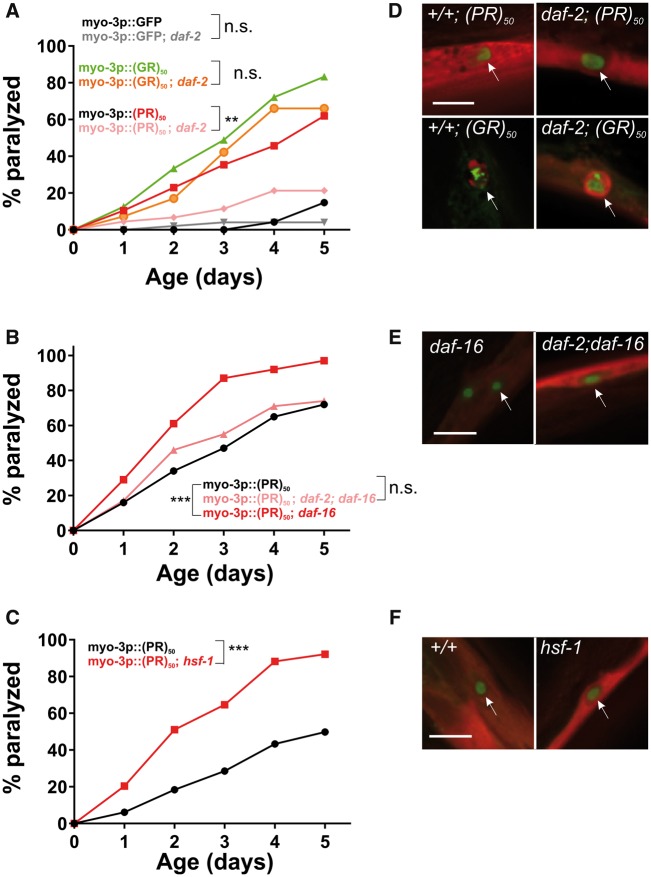
Figure 7.
Altering the rate of aging affects (PR)50 but not (GR)50 toxicity. (A) Paralysis assay of animals expressing GFP, (GR)50 or (PR)50 under the control of the myo-3 promoter in the wild-type or daf-2(e1370) background. ‘Day 0’ animals were isolated as L4 stage animals. N = 48–50 animals per genotype. n.s., ‘not significant’; **P < 0.01 versus GFP control (Log-rank test with Bonferroni adjusted P-value). (B) Paralysis assay of animals expressing (PR)50 under the control of the myo-3 promoter in the wild-type, daf-16(mu86), or daf-2(e1370); daf-16(mu86) background. N = 48–50 animals per genotype. n.s., ‘not significant’; ***P < 0.001 versus (PR)50 (Log-rank test with Bonferroni adjusted P-value). (C) Paralysis assay of animals expressing (PR)50 under the control of the myo-3 promoter in the wild-type or hsf-1(sy441) mutant background. N = 48–50 animals per genotype. ***P < 0.001 versus wild-type (Log-rank test with Bonferroni adjusted P-value). (D) Fluorescent microscopy images of day 1 adult worms expressing either (GR)50 or (PR)50 (green) and soluble muscle mCherry (red) in the wild-type or daf-2(e1370) mutant background. Arrow points to site of nuclear DPR accumulation. Scale bar=10 μm. (E) Fluorescent microscopy images of Day 1 adult worms expressing (PR)50 (green) and soluble muscle mCherry (red) in the daf-16(mu86) or daf-2(e1370); daf-16(mu86) mutant background. Arrow points to site of nuclear DPR accumulation. Scale bar=10 μm . (F) Fluorescent microscopy images of day 1 adult worms expressing (PR)50 (green) and soluble muscle mCherry (red) in the wild-type or hsf-1(sy441) mutant background. Arrow points to site of nuclear DPR accumulation. Scale bar=10 μm.