Figure 5.
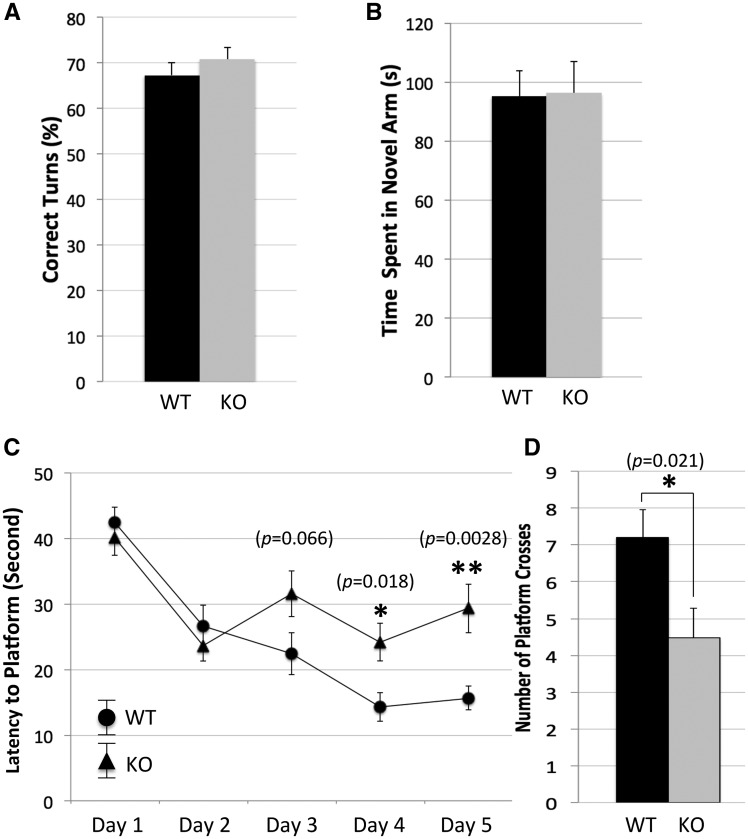
Frmpd4-KO mice show normal spatial working memory but a defective spatial reference memory. The Y-maze tests for spatial working memory include Spontaneous Alternation and Blocked Arm tests. (A) Spontaneous Alternation: the test mouse was placed at the end of one arm and remained in the maze for 5 min. The total number of correct alternations divided by the number of total possible alternations was recorded and analyzed. (B) Blocked Arm test: one of the three arms was blocked, the test mouse was allowed to explore the 2 unblocked arms for 5 min followed by rest for 10 min. The test mouse was returned to the maze with all 3 arms open and allowed to explore for another 5 min. Data was analyzed for time spent in the arm blocked during the second trial (novel arm) and presented as mean ± SEM. t-test was used to compare data between frmpd4-KO mice (n = 15) and WT littermates (n = 15). *P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Note that no significant difference was identified between WT and frmpd4-KO in these tests suggesting a normal working memory function. Morris water maze is used to test hippocampus dependent spatial reference memory. (C) Training trials: mice were subjected to four, 1-min swim trials each day in the water maze to locate a hidden platform using multiple spatial signs. The time to reach the platform is an average of 4 trials for each mouse, n = 15 mice per group. Note that frmpd4-KO mice showed slow progression in reducing time needed to locate the platform compared with WT. (D) Probe trial: after the training trial, mice were subjected to one 3-min trial of free swimming in maze without the platform. Time spent probing the quadrant where the platform was located during training trial and total number of crosses to the platform region were automatically tracked and compared between frmpd4-KO and WT control mice. Note the reduced number of crosses to the platform site in the frmpd4-KO. MEAN ± SEM was presented. t-test was used to compare data at each test point between WT and frmpd4-KO mice. *p< 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Note frmpd4-KO mice (n = 15) showed significantly reduced number of crosses to the platform site compared with WT littermates (n = 15) suggesting a deficit in the spatial reference memory function.