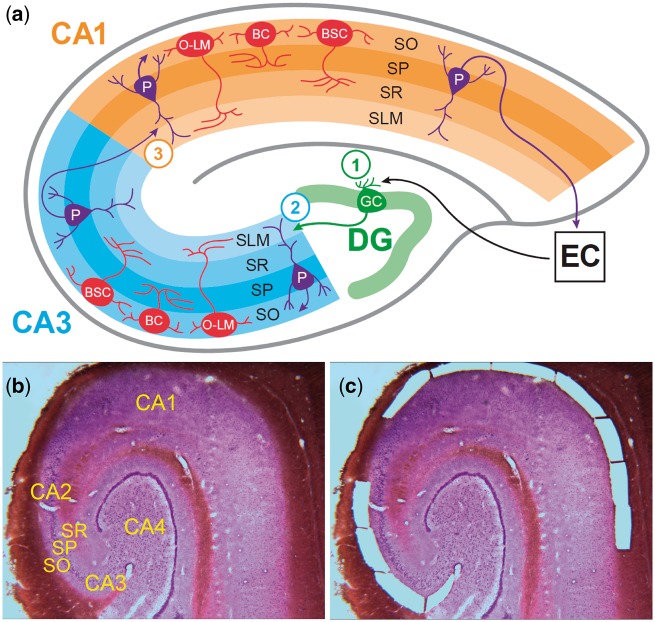
Figure 1.
Hippocampus cytoarchitecture and microdissection of stratum oriens tissue from CA3/2 and CA1. (A) The schematic depicts the cytoarchitecture of the human hippocampus, focusing on the neurons of SO and the projections of pyramidal neurons of SP. Within the SO, neurons are exclusively GABAergic and primarily fall into three subtypes: basket cells, with axons synapsing with pyramidal cell somata within SP; bistratified cells, with axons synapsing with pyramidal cell dendrites within layers SO and SR; and oriens-lacunosum-moleculare cells, with axons synapsing with pyramidal cell dendrites in the SLM. The organization of the trisynaptic pathway is depicted, and the circled numbers indicate the location of the three synapses within this prototypical hippocampal circuit. Synapse 1 occurs between projections from the entorhinal cortex layers II and III to the neurons of the dentate gyrus via the perforant pathway. Projections from the dentate gyrus (mossy fibers) to the pyramidal neurons of CA3 form synapse 2. Synapse 3 occurs between projections from CA3 pyramidal neurons (Schaffer collaterals) and pyramidal neurons of CA1. The major populations of SO GABAergic interneurons of CA3 and CA1 are the same; what distinguishes these neuronal populations is their functioning within separate microcircuits supporting the function of the second and third synapses within the trisynaptic pathway. Shown at bottom is a single Nissl-stained 30 µm section of postmortem human hippocampus before (B) and after (C) laser microdissection of tissue from stratum oriens of subfields CA3/2 and CA1. SO, stratum oriens; SP, stratum pyramidale; SR, stratum radiatum; SLM, stratum lacunosum-moleculare; P, pyramidal neuron; BC, basket cell; BSC, bistratified cell; O-LM, oriens-lacunosum-moleculare cell; DG, dentate gyrus; EC, entorhinal cortex.