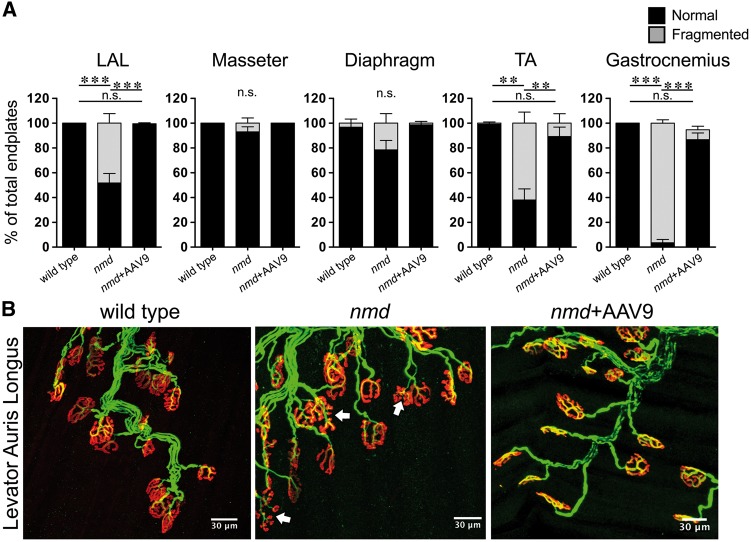
Figure 4.
End plate fragmentation is present in nmd muscles regardless of resistance to NMJ denervation. (A) Quantification of percent normal and fragmented end plates in muscles from 8-week wild-type, nmd, and nmd+AAV9-IGHMBP2 treated mice. End plate fragmentation in various selected muscles with differential vulnerability to NMJ denervation encompassing neck, trunk, and distal appendages. AAV9-IGHMPB2 treatment of nmd mice prevents end plate fragmentation in all muscles analyzed. (B) Representative images of immunostained muscle showing presence of end plate fragmentation (arrows) in a muscle resistant to NMJ denervation (cLAL) and prevention of end plate fragmentation by AAV9-IGHMBP2 treatment. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by a Bonferroni post hoc test for multiple comparisons. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.001; ***P < 0.0001. n.s., not significant. n = 3 animals per treatment.