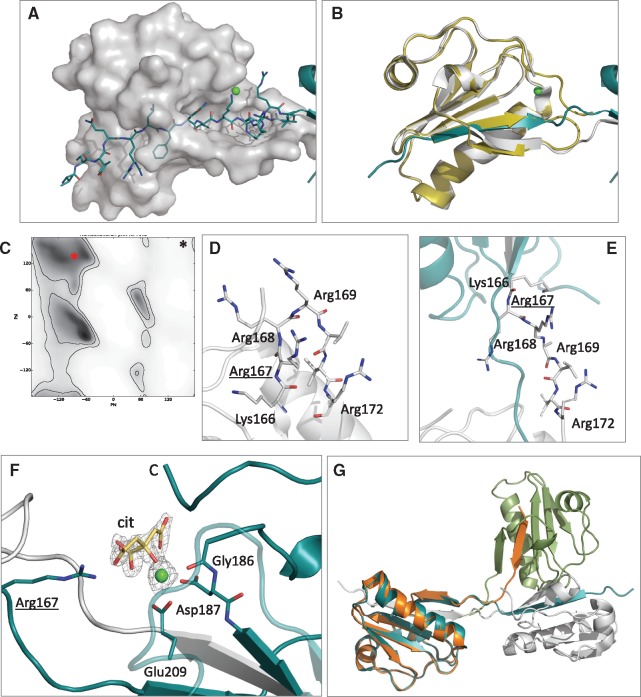
Figure 2.
Details and characteristics of the domain-swap dimer. (A) Interactions between Chain A (transparent surface) and swapped strand β1 of Chain B (cyan sticks). (B) Superposition of wt monomer (yellow cartoons) with chain A of the Gly167Arg dimer (white cartoons). (C) Ramachandran plot for arginines (gray gradient indicates most favorable angles), the red asterisk shows the position of Arg167 in the dimer (from the reported structure) while the black symbol the corresponding Gly167 in the wt monomer. (D and E) Zoom view of the hinge loop in a model of the mutant monomer and in the crystal structure of the domain-swapped dimer. Positively charged residues hosted by the segment are shown as sticks. (F) The calcium-binding site in the Gly167Arg dimer showing the calcium ion (green sphere), chelating residues (sticks) and Arg167 that forms a H-bond with the citrate molecule (cit., in yellow). All residues are labeled. 2Fo-Fc electron density, contoured at 1.5σ, for calcium and citrate is also visible as a gray grid. (G) Superposition of chain A of the dimer (cyan and white cartoon) with chain A of the lower resolution monoclinic structure (green and orange), to highlight differences in the relative orientation of the monomers in the two crystals.