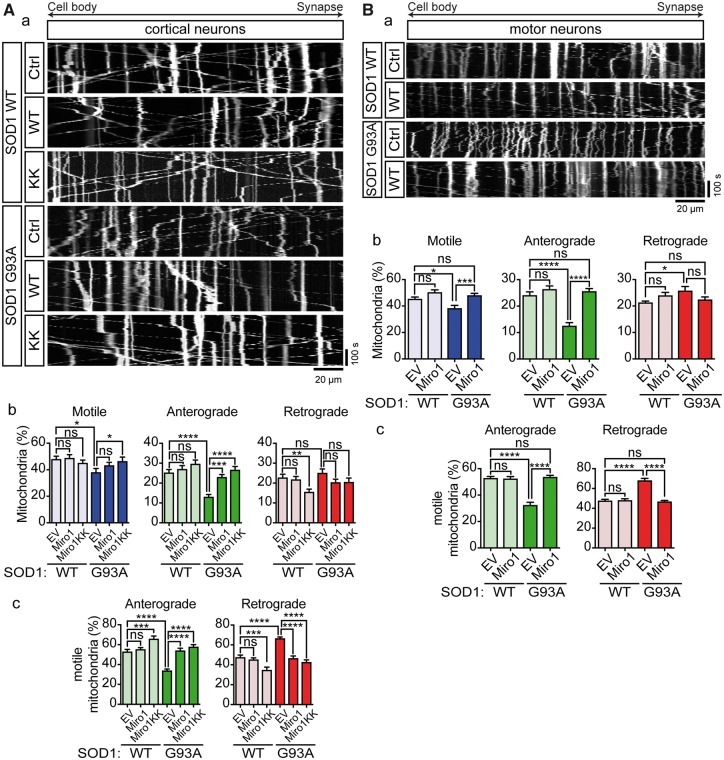
Figure 4.
Expression of Miro1 rescues axonal transport of mitochondria in ALS mutant SOD1 expressing neurons. (Aa, Ba) Kymographs show transport of mitochondria in rat cortical neurons and motor neurons co-expressing EGFP-SOD1 WT or G93A with empty vector (Ctrl), myc-Miro1 (WT), or Myc-Miro1E208K/E328K (KK). (Ab, c; Bb, c) Quantitative analysis of mitochondrial transport shows that expression of ALS mutant SOD1 significantly impairs overall motility of mitochondria (Ab, Bb—Motile) because of a selective block of anterograde (Ab, Bb—Anterograde), but not retrograde transport (Ab, Bb—Retrograde). As a consequence, SOD1 G93A disturbed the balance of transport to inhibit anterograde and promote retrograde movement (Ac, Bc). Co-expression of myc-Miro1 WT or KK, fully rescued impaired transport of mitochondria (Ab, Bb) and rebalanced anterograde and retrograde transport (Ac, Bc). Results are shown as mean ± SEM, statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test, ns, not significant, * P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001, N (cortical neurons): SOD1 WT+Ctrl: 18, SOD1 WT+WT: 24, SOD1 WT+KK: 23, SOD1 G93A+Ctrl: 20, SOD1 G93A+WT: 24, SOD1 G93A+KK: 22 from 4 experiments; N (motor neurons) = WT+Ctrl: 15, SOD1 WT+WT: 16, SOD1 G93A+Ctrl: 19, SOD1 G93A+WT: 29 from 5 experiments.