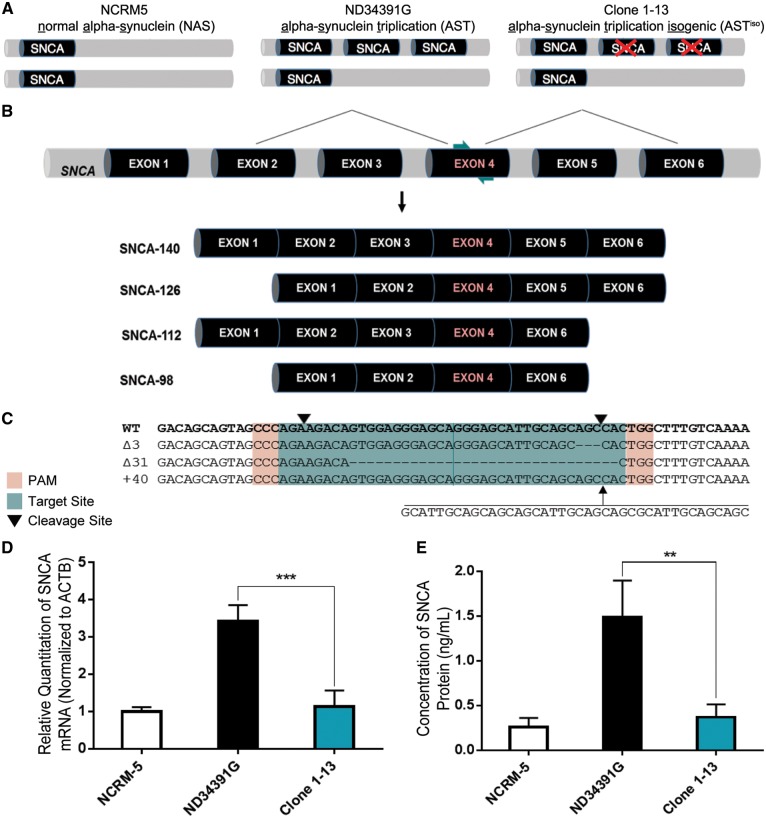
Figure 1.
Double Knockout of SNCA in iPSCs Derived from a PD Patient with SNCA Triplication via Double-Nicking CRISPR/Cas9. (A) Schematic representation of normal alpha synuclein (NAS), alpha-synuclein triplication (AST) and alpha-synuclein triplication isogenic (ASTiso) iPS lines. The triplication involves a large Mb region including the SNCA gene. (B) Position of sgRNAs (teal arrows) guiding Cas9 nickases to SNCA exon 4, common to all four α-synuclein transcript isoforms. (C) Wild-type, 3 bp deletion, 31 bp deletion, and 40 bp insertion alleles identified by sequencing of Clone 1-13. PAMs are highlighted in red, sgRNAs in teal and downward pointing black arrows represent cleavage sites. (D) qRT-PCR for total SNCA mRNA shows a normalization of α-synuclein transcript levels in Clone 1-13 iPSCs. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. (E) ELISA shows a normalization of α-synuclein protein levels in Clone 1-13 iPSCs. Data are represented as mean ± SEM of biological triplicates. **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001. See also Supplementary Material, Figs S1 and S2 and Table S4.