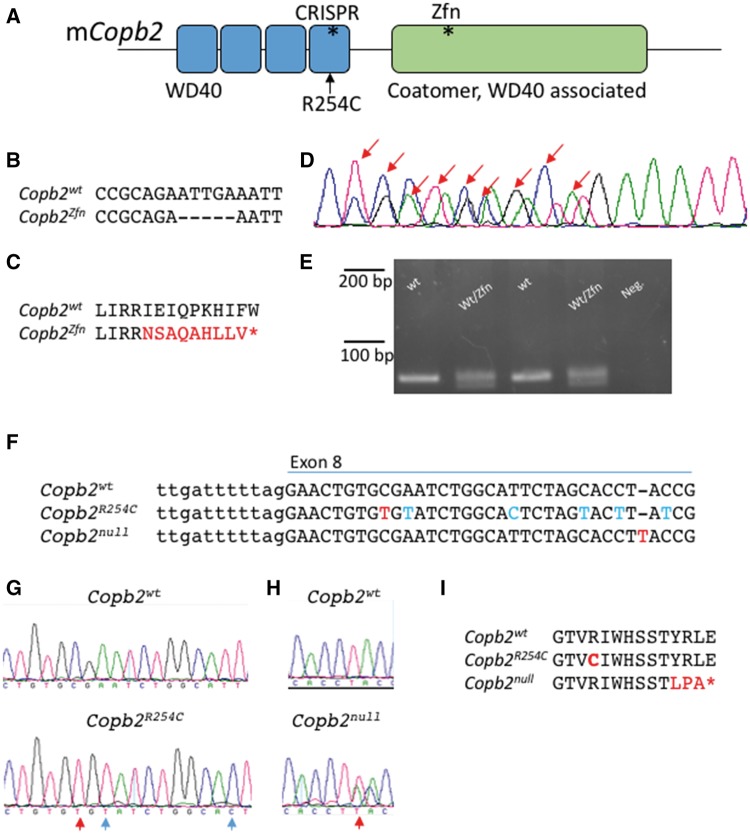
Figure 2.
Mouse alleles of Copb2. (A) Schematic of the mouse COPB2 protein domains. Asterisks denote sites of mutations. (B–E) The Copb2Zfn allele is a 5 bp deletion in exon 12 (B, D), which results in a frameshift and creates a premature stop codon (C). (D) Sanger sequencing of the PCR products from a heterozygous animal. Sanger peaks that differ from wild-type are indicated by red arrows and this analysis identifies the precise nature of the deletion. (E) Genotyping was performed by PCR amplification of a 79 bp region surrounding the deletion and gel electrophoresis (4% metaphor agarose). (F–H) The Copb2R254C (F, G) and Copb2null (F, H) alleles were created using CRISPR-Cas9 technology targeting exon 8. Red letters indicate nucleotide changes affecting the amino acid sequence while blue letters indicate silent mutations. (I) Copb2R254C creates an amino acid change orthologous to the patient mutation at amino acid position 254, while Copb2null creates a frameshift resulting in a premature stop codon (*) at position 264.