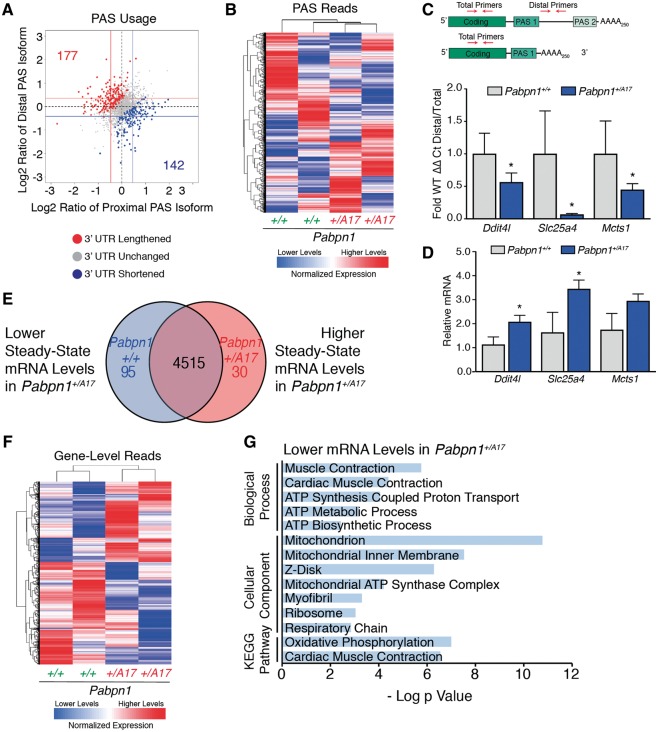
Figure 4.
3' READS reveals modest changes in poly(A) signal usage in Pabpn1+/A17 mice. (A) Scatter plot depicting that few changes were detected in poly(A) sequence (PAS) selection by 3’ READS performed on RNA isolated from rectus femoris (RF) muscles from three-month-old male Pabpn1+/A17mice. Data are log2 ratio of distal to proximal PAS usage with increased distal PAS represented in red and increased proximal PAS represented in blue. n = 2 mice per genotype. (B) Sample clustering based on PAS usage as detected by 3'READS performed on RNA isolated from RF muscles of three-month-old mice showing that Pabpn1+/+ and Pabpn1+/A17 mice group by genotype. (C) Candidate genes validated for change in PAS selection and steady-state levels by qRT-PCR. Altered PAS selection was calculated as ΔΔCt of distal primer PCR product relative to total transcripts as detected by coding sequence primers and are reported in Pabpn1+/A17 mice as a fraction of wild type. (D) Steady-state levels of candidate genes as analyzed by qRT-PCR. All transcripts were normalized to Gapdh. *P < 0.05. (E) Venn diagram depicting changed steady-state mRNAs in RF from three-month-old Pabpn1+/A17. Of 4515 genes detected, 95 were depleted and 30 were increased. (F) Sample clustering showing that based on steady-state mRNA levels, Pabpn1+/+ and Pabpn1+/A17 mice group by genotype. (G) Histogram of the log P value of top GO terms and KEGG pathways for mRNAs decreased in Pabpn1+/A17mice revealing decreased levels of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial mRNAs.