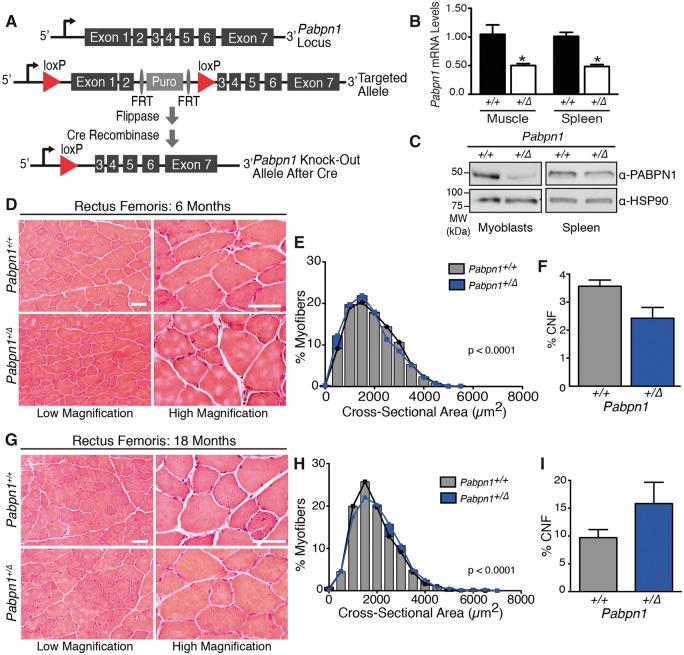
Figure 6.
Age-related hypertrophy in Pabpn1+/Δ knock-out mice. (A) Schematic of Pabpn1 knock-out allele. Before Cre recombinase-mediated recombination, the targeted allele contains a puromycin resistance gene flanked by FRT elements between exons 2 and 3 of the Pabpn1 locus. The FRT-flanked puromycin resistance gene and exons 1 and 2 of Pabpn1 are surrounded by loxP sites. After flippase and Cre-mediated recombination, exons 1 and 2 of Pabpn1 are excised resulting in a null allele with no start codon. (B) Steady-state Pabpn1 mRNA levels were decreased by ∼50% in muscle and spleen from 3-month-old male Pabpn1+/Δmice as detected by qRT-PCR. Data are mean fold change ± SEM from n = 3 mice per genotype. *P < 0.05. (C) Steady-state PABPN1 protein levels were decreased by half in 3-month-old male Pabpn1+/Δmice as detected by immunoblot using an α-PABPN1 antibody (41). HSP-90 was used as a loading control. (D) Histologic sections from rectus femoris (RF) muscles isolated from six-month-old male Pabpn1+/+ and Pabpn1+/Δ mice shown at low and high magnification. Bar = 50 µm. (E) Significantly smaller myofiber cross-sectional area (CSA) was detected in RF muscles from six-month-old Pabpn1+/Δ mice. Data are the frequency distribution of myofiber CSA. (F) No significant difference detected in the percentage of centrally nucleated fibers (CNF) from RF sections from six-month-old male Pabpn1+/+ and Pabpn1+/Δ mice. Data are mean ± SEM. (G) Histologic sections from RF muscle isolated from 18-month-old male Pabpn1+/+ and Pabpn1+/Δ mice shown at low and high magnification. Bar = 50 µm. (H) Significantly larger CSA was detected in RF muscles from 18-month-old male Pabpn1+/Δ mice. Data are the frequency distribution of myofiber CSA. (I) No significant difference was detected in the percentage of centrally nucleated fibers (CNF) from RF sections from 18-month-old male Pabpn1+/+ and Pabpn1+/Δ mice. Data are mean ± SEM. In all cases, n = 5 mice per genotype.