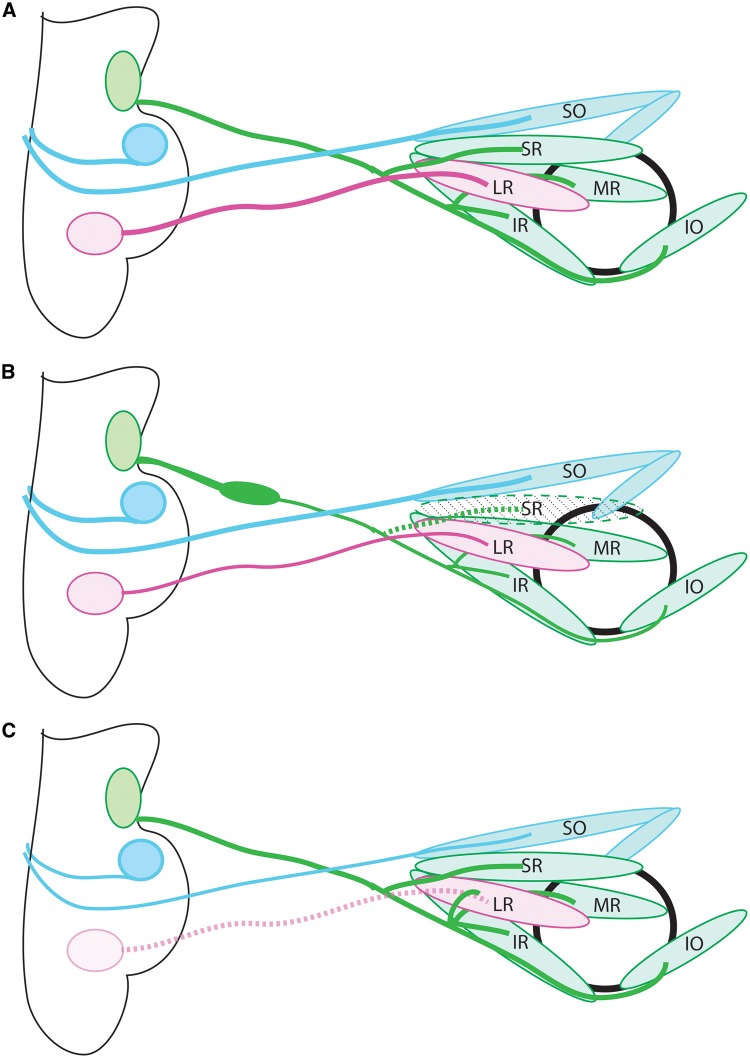
Figure 1.
Anatomy of the ocular motor system. (A) Schematic of the normal anatomy of the ocular motor system. The oculomotor nerve (cranial nerve 3; green) extends from the midbrain to the orbit, where it then divides into superior and inferior divisions and innervates the SR and LPS (not shown), and the IR, MR, IO, respectively. The trochlear nerve (cranial nerve 4; blue) exits the midbrain dorsally, crosses the midline in the tectum, then innervates the contralateral SO. The abducens nerve (cranial nerve 6; pink) exits the hindbrain and innervates the LR. (B) CFEOM1 pathology. The superior division of CN3 is absent, and the nerve displays a proximal bulge formed by stalled, misdirected axons, followed by distal thinning. The SR and LPS (not shown) are hypoplastic. CN4 appears normal and CN6 has mild thinning. (C) Duane syndrome pathology. CN6 is absent, and there is misinnervation of the lateral rectus by axons of CN3. CN3, oculomotor nerve; CN4, trochlear nerve; CN6, abducens nerve; SO, superior oblique; SR, superior rectus; MR, medial rectus; IR, inferior rectus; LR, lateral rectus; IO:= inferior oblique.