Figure 4.
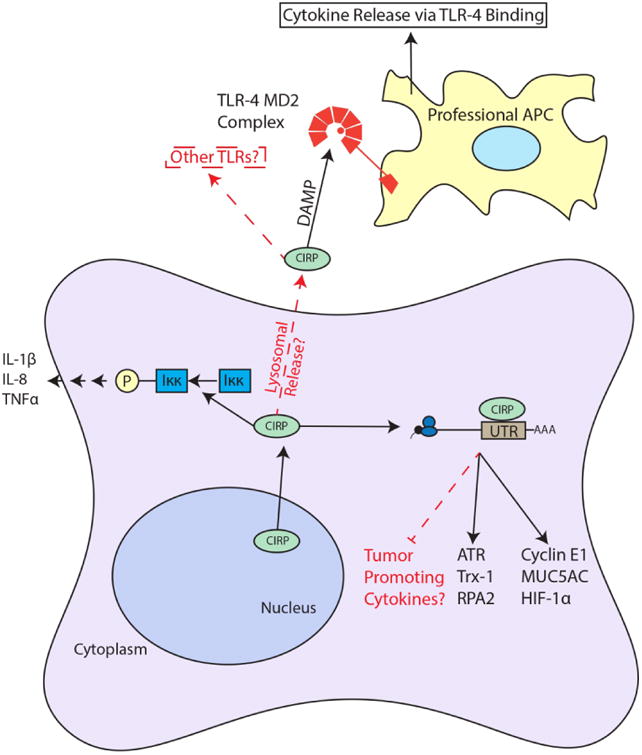
Summary of CIRP Roles in Inflammation and Cancer. CIRP shuttles from the nucleus to the cytoplasm to bind the 3′ UTRs of target mRNA to increase their translation. It is possible that CIRP can bind tumor promoting cytokines in certain contexts. CIRP in found extracellularly in patients with sepsis (likely through lysosomal secretion) where it binds the TLR-4 MD2 complex, functioning as a DAMP and stimulating cytokine release from APCs. Also, CIRP increases Iκκ phosphorylation through an unknown mechanism. Arrows and boxes in black represent known roles from literature and red dashed arrows and boxes represent possible mechanisms or connections.
