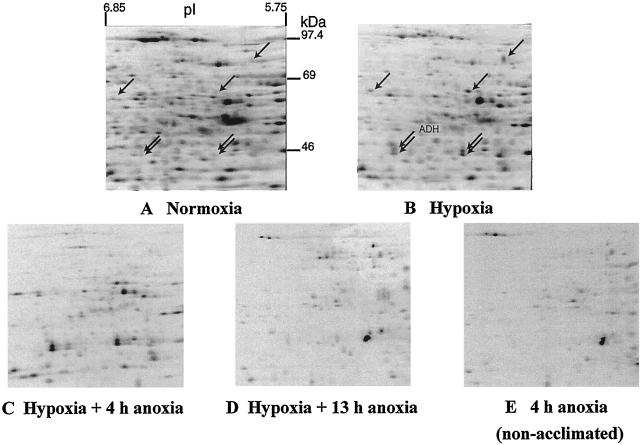
Figure 2.
Effects of low-O2 treatments on patterns of protein synthesis in intact maize root tips. Data are fluorographs of root tip proteins, labeled in vivo with [35S]Met and separated by two-dimensional IEF-SDS-PAGE. Fifteen 6-d-old (post imbibition) seedlings were labeled with [35S]Met during the last 4 h of each treatment. A, Normoxia, 8 h under 100% (v/v) O2. B, Hypoxia, 4 h of O2, 4 h of 3% (v/v) O2. C, Hypoxia plus 4 h of anoxia, 4 h of O2, 4 h of 3% (v/v) O2, 4 h of N2. D, Hypoxia plus 13 h of anoxia, 4 h of O2, 4 h of 3% (v/v) O2, 13 h of N2. E, 4 h of anoxia, 8 h of O2, 4 h of N2 (non-acclimated). Root tip proteins (100 μg per sample) were fractionated by two-dimensional IEF-SDS-PAGE, and labeled proteins were visualized by fluorography using an exposure time of 95 h. Arrows in A and B point to proteins that were induced greater than 2-fold by hypoxic treatment. ADH was identified by western blot and confirmed by MS.