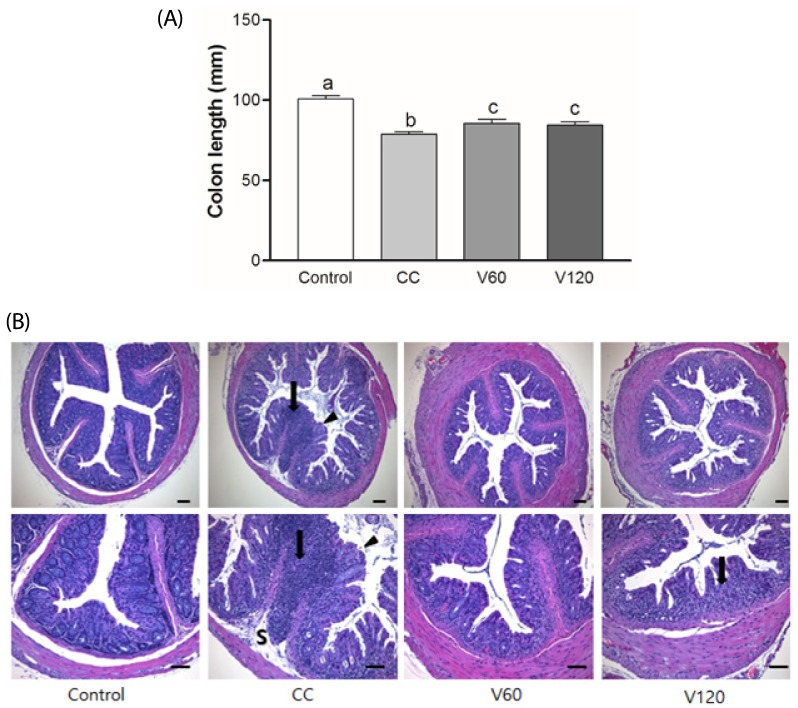
Fig. 2. Effects of vitamin C supplementation on colon length and histology in colitis-associated colon cancer.
(A) Colon length was measured and compared among four groups. Mean ± SEM are shown (Control, n = 9; CC, n = 12; V60 and V120, n = 11 per group). One-way ANOVAs and Newman-Keuls' post hoc tests were performed (P<0.05). (B) Representative histologic sections of distal colon from among four groups. Glandular epithelium destruction (arrow head), neutrophil infiltration (arrow) or submucosa extension (S) were shown. HE stain, bar = 100 µm. Magnification, upper 100x, lower 200x CC, AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer; V60, AOM/DSS + 60 mg/kg body weight (b.w.) of vitamin C; V120, AOM/DSS + 120 mg/kg b.w. of vitamin C.