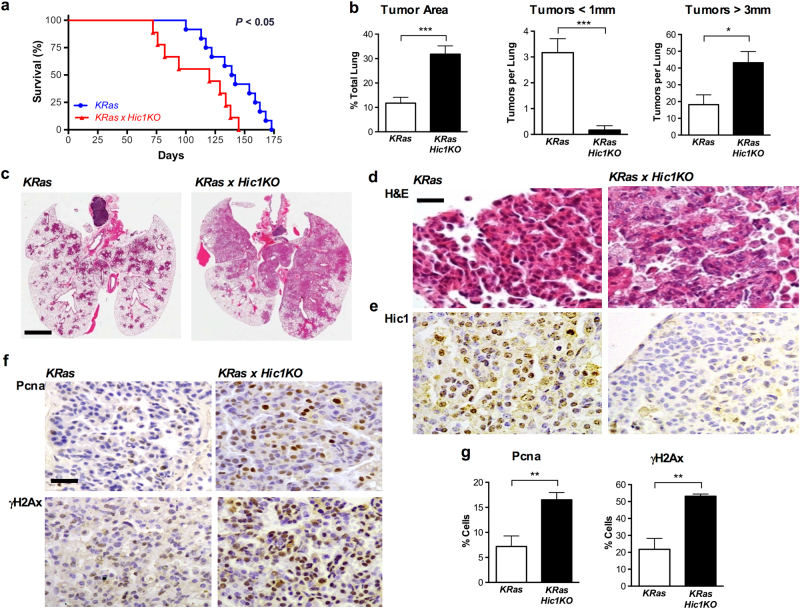
Fig. 4. Effects of Hic1 deletion (Hic1KO) on the development of lung tumors induced by the conditional activation of an activating KRasG12D (KRas) mutant in the airway epithelium of adult mice.
Mice from each geneotype were anesthetized using Avertin at a dose of 0.5 mg/gram of body weight, and administered 5 × 108 PFU Ad5CMVCre virus (Viral Vector Core Facility, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA) by intranasal inhalation at 8 weeks of age and observed for 9 months or until ethical endpoint. a Kaplan–Meier survival analysis of KRas and KRas × Hic1 KO mice following inhalation of adenoviral Cre recombinase. n = 12 (KRas) and 9 (KRas× Hic1KO). Sample size was based on previous published studies [71]. b Quantitative analysis of lung tumor area and size in mice from the same experiment depicted in Fig. 4a. n = 6 per genotype, ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, unpaired t-test. Mouse lungs were inflated with 10% buffered formalin and fixed overnight before paraffin embedding. For quantitation of tumor burden and number, sections were scanned using the Aperio Scanscope XT (Leica Biosystems, Buffalo Grove, IL, USA) and analysed using Aperio Imagescope software by a blinded observer as described [71]. Sample size was chosen based on previous studies [71]. c Representative photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained sections of lungs from the experiment depicted in Fig. 4a. Scale bar = 5 mm. d Representative high-powered photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained sections of lungs from the same experiment. Scale bar = 20 μm. e Representative photomicrographs of sections from the same tumors stained with immunoperoxidase (brown) for Hic1, and countersained with hematoxylin (blue). Immunohistochemistry was performed as described [71]. f Immunstaining for Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (Pcna, Dako, Troy, MI, #M087901-2) or phospho-γH2AX (γH2AX, Abcam, Cambridge, UK) in the same tumors shown in Fig. 4d. Immunohistochemistry and quantitifcation of staining was performed as described [71]. Scale bar = 100 μm. g Quantitative analysis of Pcna and γH2AX staining from the same experiment depicted in Fig. 4f. n = 5 per genotype, 5 fields of view at 40× counted per animal. **P < 0.01, unpaired t-test