Figure 4.
Building Predictive Models of Rat Perceptual Choices
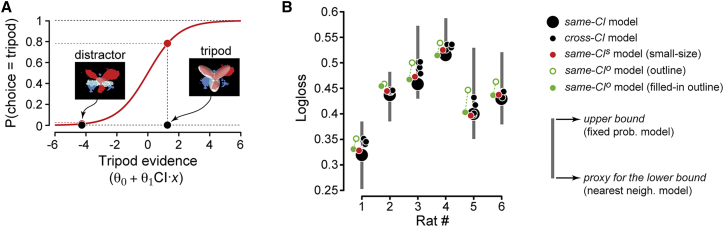
(A) Illustration of how the classification image obtained for rat 1 was combined with logistic regression to (1) infer the evidence gathered by the animal about an arbitrary input image being the tripod (abscissa axis); and (2) translate this evidence into a probability of choosing the tripod category (ordinate axis).
(B) The accuracy of various models in predicting rat responses to the full-body, regular-size random tripods is measured using a logloss function (see STAR Methods). Predictions of five different models are shown (see caption on the right), which differed according to the classification images that were plugged into Equation 1 (see Results). The logloss values obtained by constant-probability and nearest-neighborhood response models are also shown, to provide, respectively, an estimate of the logloss’s upper bound and a proxy of its lower bound (gray bars).
See also Figures S2, S3, and S5.